Description
Properties
Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae is a mold (watering can mold) that plays a major role in Japanese cuisine. It is the most important among the Kōji fungi.
It is used to ferment soy in solid bioreactors to produce miso and soy sauce. The delicacy Daitokuji-Nattō, which originated in Kyōto, is also made with Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae inoculated soybeans. Is used to make sake, yellow kōji is extremely sensitive to temperature; its moromi can become slightly sour during fermentation. Mainly white and black kōji are used in shōchū production, while only yellow kōji (A. oryzae) is often used in sake production.
A. flavus var. oryzae is one of the main industrial sources for the production of starch-degrading α-amylases. It is one of the organisms that are fully gene sequenced.
Although it has no specific common name, it can also be recognized as the “aflatoxin producer”. Aflatoxin is a toxic and carcinogenic compound produced by A. flavus.
1. Growing
Growing Procedure
Aspergillus flavus has the capacity to grow on many nutrient sources. It is mainly a saprophyte and grows on dead plant and animal tissue in the soil, which is important for the recycling of nutrients. Because it grows well on decaying vegetation, one common place you might find Aspergillus is in compost or on fallen leaves. However, this fungus is also a parasite and can use living organisms as hosts. Host species include corn, peanuts, nut trees, cotton, and even humans.
Typically this organism favors hot, dry conditions which makes it unique in comparison to other fungi. The best temperature for growth is 37°C (98.6°F). However, it can grow at any temperature between 12-48°C (54-118°F). Aspergillus flavus is omnipresent in nature but has a more limited growth indoors. Aspergillus molds thrive best in oxygen-rich environments and also on materials that are rich in carbon which they feed off of for nutrients.
Aspergillus oryzaecan often be found growing inside dirty air conditioners inside of buildings or in your own home. This has even been known to be a problem in some hospitals. Aspergillus may also grow on or inside walls in homes, especially if the house is damp or has been damaged by flooding.
Growing
Agar Culture Media: PDA
Cropping: 72h
Containers for fruiting: clean bowl
Biological efficience:
Substrates: Starter: 4g ground millet, 2ml water + soybeans/grains/rice/legumes.
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp °C |
30-35 | you use only the spawn of this mushroom |
|
Relative Humidity % |
60-80 | ||
Duration d |
3 | ||
CO2 ppm |
>10000 | ||
FAE per h |
0-1 | ||
Light lux |
– |
Affiliate Partner
Natural Habitat
Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae is a pathogenic fungus whose spores are ubiquitous in nature. It can cause aspergillosis in animals and humans.
Growing Characteristics
To prepare koji, mix:
-350 g washed soybeans. Washed and soaked for 15 hours, crushed and steamed for 30 minutes Drain for 4h
-300g roasted, then crushed millet
4ml liquid culture or starter, incubate at 30°C for 72 hours, stir twice a day. Never higher then 45°C.
2. Identification
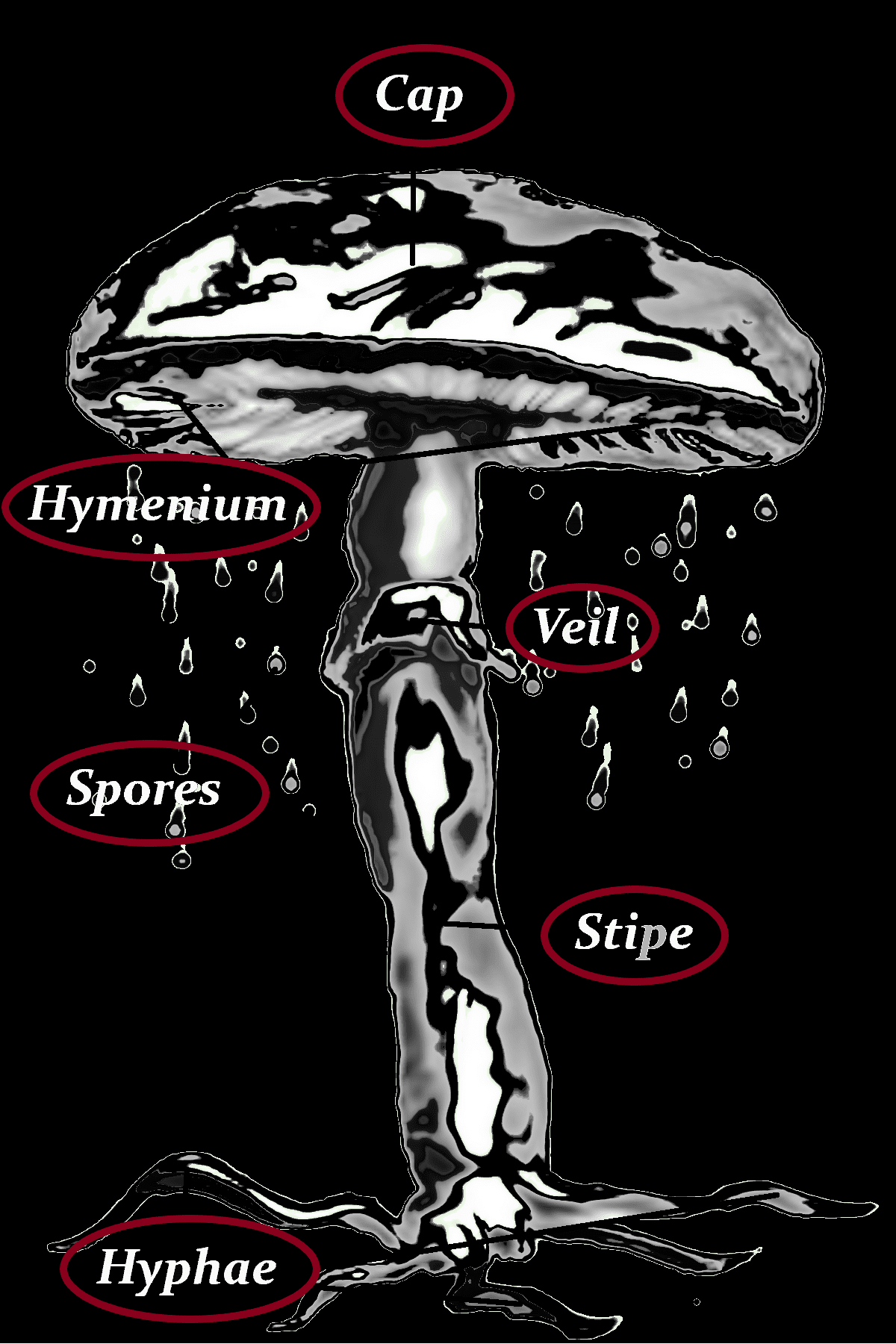
Cap
Hymenium
–
Veil
–
Stipe
–
Hyphae
-white and then yellowish white
-then yellowish
-finally the greenish-yellow color dominates
Spores
–
Danger of confusion
other koji mold
© blatest
3. Consuming
Gourmet
Aspergillus oryzae strength is that it produces a rich, fruity, and refreshing flavor, so it is still used by some producers despite the difficulty and great skill it requires.
Flesh
greenish-yellow
Taste
from this one Sake is made, Koji-rice is sweet
Smell
koji
Nutritional content
.
4. Data med, edible
other names
Aspergillus flavus var. oryzae, Nihon Kōjikabi, kōjikin, Hefe-Pilz, 麴霉菌 / 曲霉菌, [麴菌/曲菌], Pinyin qūmeíjūn, 누룩곰팡이, nurukgompangi, Gießkannenschimmel
| Tschechisch | kropidlák rýžový |
| Wissenschaftl. Name | Aspergillus flavus oryzae |
| Wissenschaftl. Name | Aspergillus oryzae |
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division | Ascomycota |
| Class | Eurotiomycetes |
| Order | Eurotiales |
| Family | Trichocomaceae |
| Genus | Aspergillus |
| Species | A. flavus var. oryzae |
| Ecology |