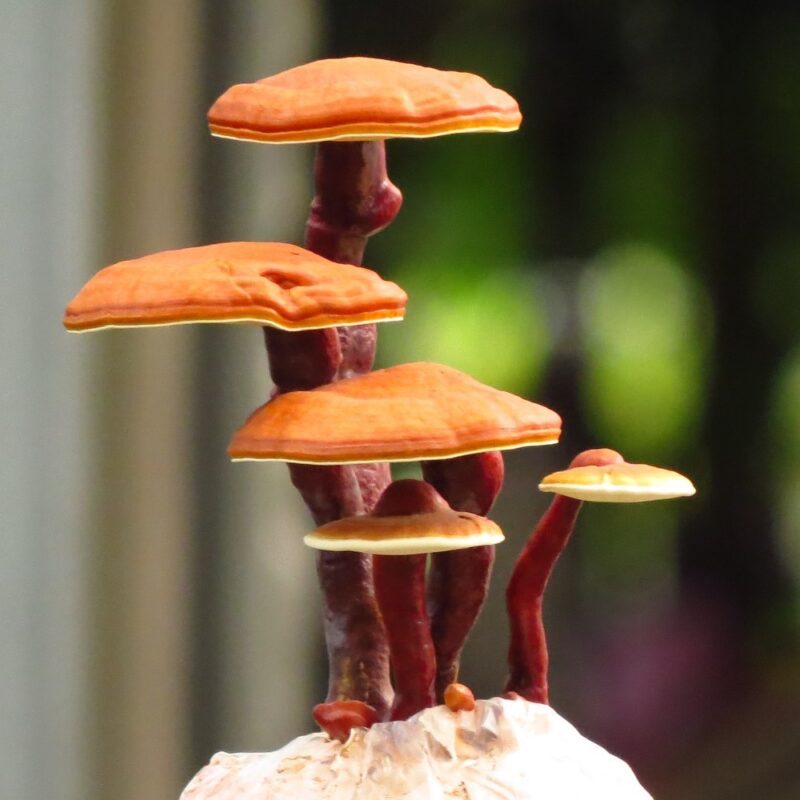
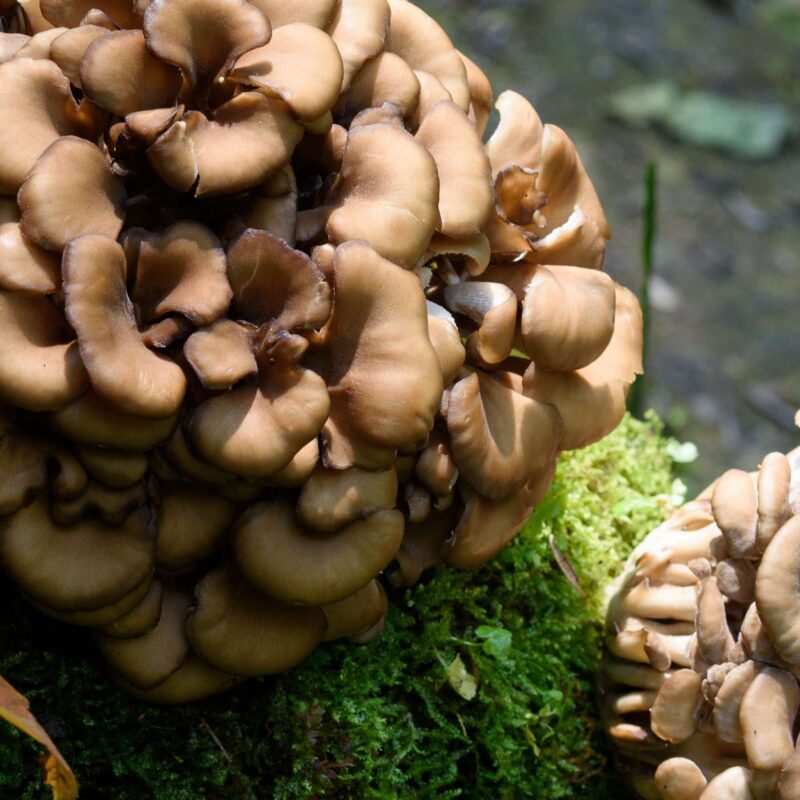
Description
Properties
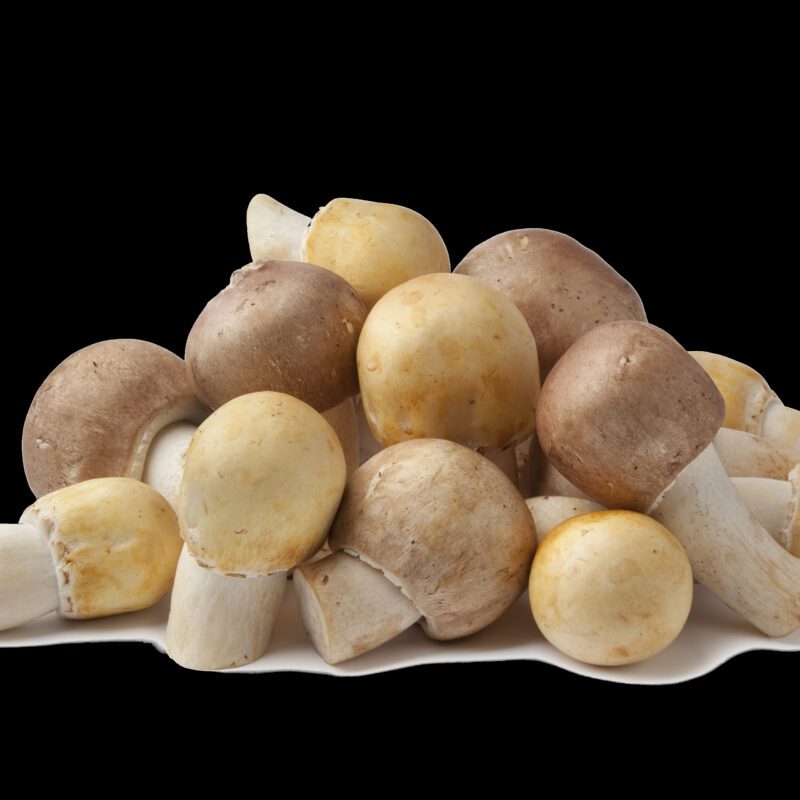
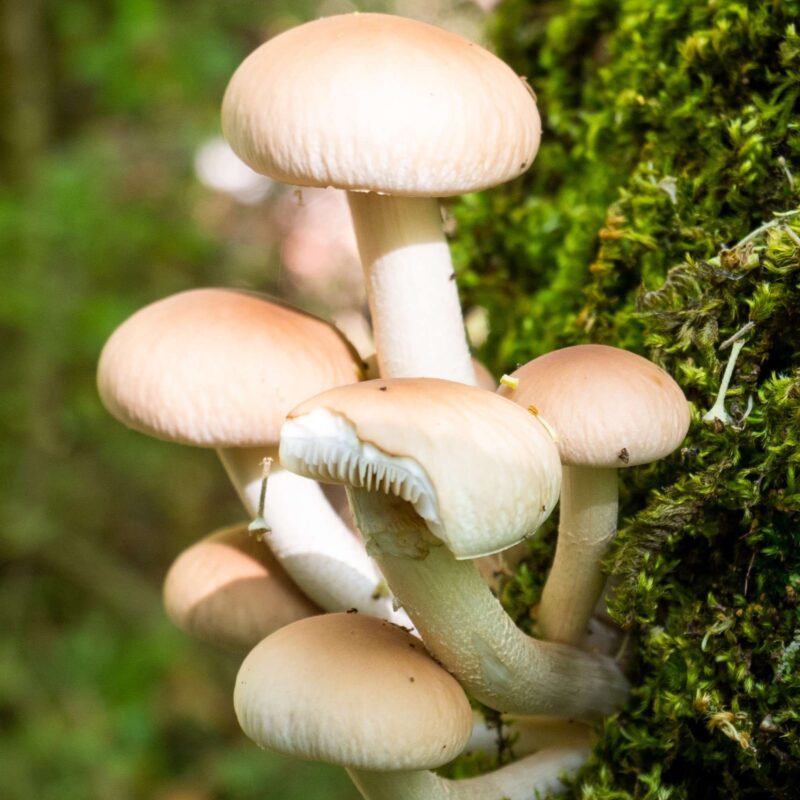
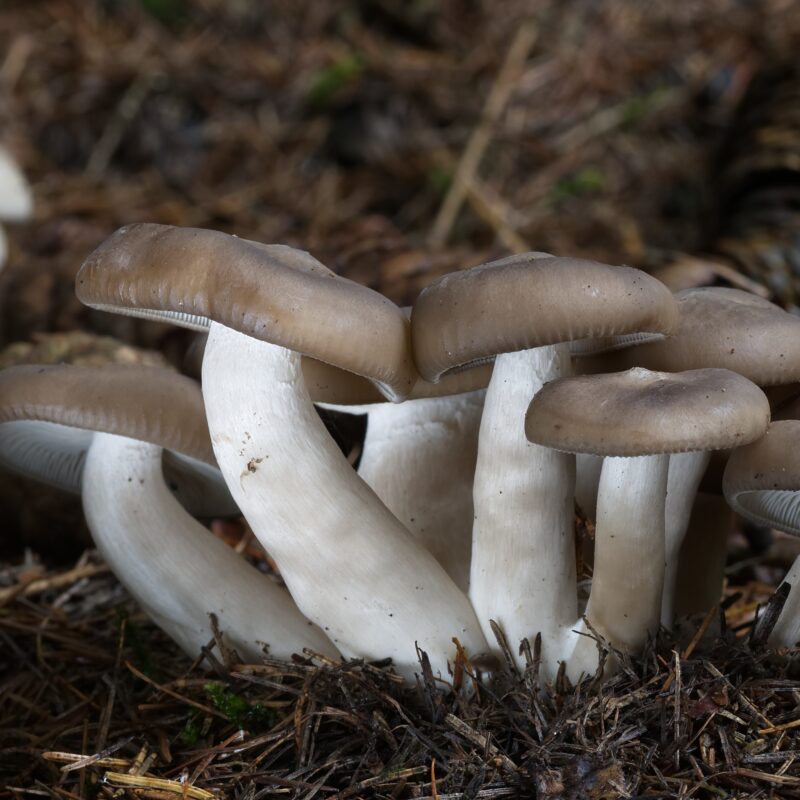
The elm or hardwood mushroom (Hypsizygus ulmarius) is a species of fungus in the Tricholomataceae family.
Hypsizygus ulmarius is a relatively rare parasite that prefers to attack weakened elms and, more rarely, other deciduous trees. After the tree dies, it switches to a saprophytic lifestyle.
“True” cultures of Hypsizygus ulmarius are unfortunately very rare. Many dealers will sell you as “elm side fungus”, or “elm oyster” under a false Latin name a side fungus species from the northwestern USA, mistakenly dubbed Hypsizygus ulmarius due to a mix-up. The common name “Elm oyster” in the English-speaking world did the rest to spread the confusion unintentionally.
The elm oyster is edible. Since its occurrence has declined sharply in recent years, the species should be protected.
The relatively rare Hypsizygus ulmarius grows parasitically on living or freshly felled deciduous trees, especially elms. It produces a white rot in the substrate. The tufted fruiting bodies often appear on living trunks at a height of several meters.
The variety now known in specialist circles as “pseudo elm oyster” was commercially successful for many years because it fructifies quickly and produces high yields. But Hypsizygus ulmarius never forms run-down lamellae as the “pseudo elm oyster” does.
1. Growing
Growing Procedure
Breeding attempts of Hypsizygus ulmarius are hardly documented, but this is probably more due to the problems mentioned above and the relative rarity of the species. Unsterile on elm logs or sterile on a substrate containing elm wood and high-caloric aggregates (prefer to feed your elm grasslings with pure hardwood).
Expect a maturation period of several months.
Elm Oysters often benefit from scratching the surface. Unlike cultivated hybrids of other rasling species, wild elm raslings do not fruit in swarms, but as small groups of individual mushrooms.
Growing
Agar Culture Media: MEA, MYA/PDYA
Cropping: 2 harvests, 7-10 days apart
Containers for fruiting: Straw bales, tree trunks, mushroom bed, culture in greenhouse
Biological efficience: 100-200%
Substrates: Rye Berries, grain mix, Straw, coffee grounds, paper, hardwood: poplar, alder, aspen, maple, ash, beech, willow, elm, oak, birch
Growing Characteristics
Extensive, late summer to late fall, usually tufted, very rare
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp °C |
21-27 | 10-13 | 13-18 |
Relative Humidity % |
95-100 | 95-100 | 90-100 |
Duration d |
14-21 +7rest | 5-10 | 4-7 |
CO2 ppm |
>1000 | <1000 | 600-1500 |
FAE per h |
0-1 | 4-8 | 4-8 |
Light lux |
– | 500–1000 | 500-1000 |
Affiliate Partner
Natural Habitat
Hypsizygus ulmarius fruits from Oktober till November.
On alive hardwood, rarely on dead wood, likes elms
2. Identification
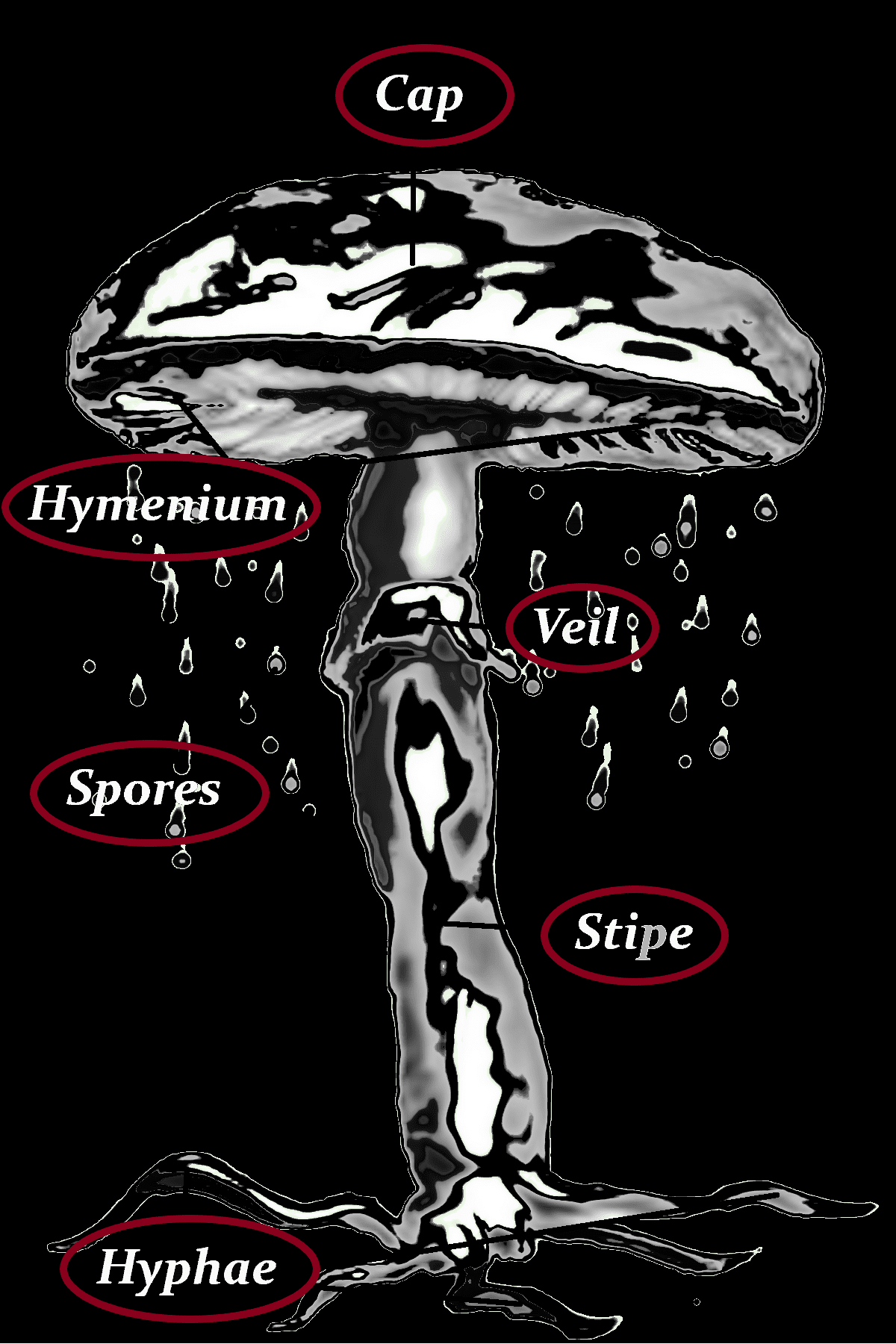
Cap
16 (25) cm Ø
-yellow ochre, pale yellow ochre, grayish yellow
-fibrous ingrown
-indented
-concentrically arranged
-cap skin with brown spots
-smooth
-often with conspicuous water spots
-round
-margin long-rolled
-brownish when old
-habitus shell-shaped
-mostly lobed
Hymenium
-whitish to creamy yellowish
-sometimes slightly decurrent
-adherent
-crowded
-with intermediate lamellae
-cut edges near the stem often strongly wavy
Veil
–
Stipe
-7-18 (20) cm long
-2-4 (5) cm Ø thick
-cylindrical
-light yellow, yellow ochre, grayish yellow
-longitudinally fibrous
-base cheerfully whitish due to mycelial filaments
Hyphae
–
Spores
-white
-round to ovoid
-3-7 x 3.9-5.5 µm
-often also filled with a large droplet
-hyaline
-smooth
-teardrop-shaped
-with four spores
-buckles present
Danger of confusion
Berindeter Seitling, Marmorierter Holzrasling, Gelbblättriger Rübling, Waldfreund Rübling
3. Consuming
Gourmet
Hypsizygus ulmarius is a tasty mushroom, which surprises with his flavours.
Flesh
white, yellowish, yellow to base, coarse, tough, fibrous
Taste
soft, sour, a bit floury-cucumbery
Smell
sour, watermelon, floury-cucumber or even herring-like
Nutritional content
.
4. Data med, edible
other names
| Dänisch | Elmehat |
| Englisch |
Elm Mushroom
|
| Finnisch |
jalavanrunkokynsikäs
|
| Finnisch |
runkovalmuska
|
| Französisch |
Lyophylle de l’orme
|
| Litauisch |
Guobinė kupstabudė
|
| Norwegisch |
almeknippesopp
|
| Russisch |
Гипсизигус ильмовый
|
| Schwedisch | almskivling |
| Tschechisch | líha jilmová |
| Ungarisch |
Laskapereszke
|
| Wissenschaftl. Name |
Hypsizygus ulmarius
|
| Wissenschaftl. Name |
Lyophyllum ulmarium
|
| Wissenschaftl. Name |
Pleurotus pantoleucus
|
| Wissenschaftl. Name |
Pleurotus ulmarius
|
other names
Ulmenrasling, Ulmenholzrasling, Ulmenseitling, Hypsizygus Ulmarius, Lyophyllum Ulmarium, Ulmenausternpilz, Shirotamogitake, Da Yu Mo, Shirotamogitake
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division | Basidiomycota |
| Class | Basidiomycetes |
| Order | Agaricales |
| Family | Tricholomataceae |
| Genus | Hypzisigus |
| Species | Hypzisigus ulmarius |
| Ecology | Parasitic |