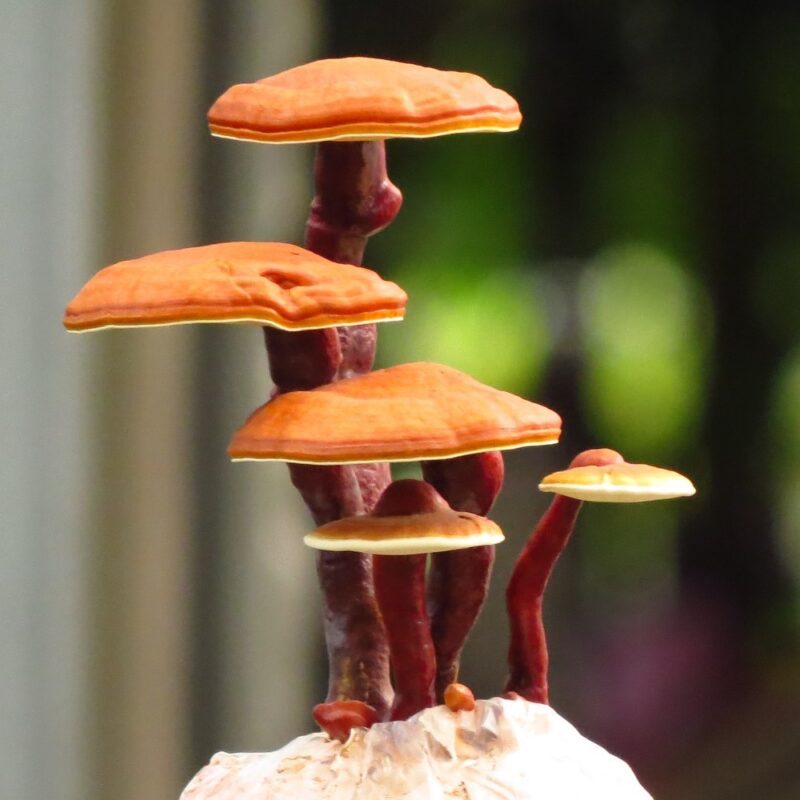
Description
Properties
Cordyceps militaris is a fungus from the tubular fungi division that parasitizes on butterfly pupae.
Cordyceps species are among the few fungi that “dock” onto insect larvae or adult hosts with parasitic intent. Cordyceps militaris, which is also found in our region, attacks pupal stages of moths deposited in the soil. All Cordyceps species are specialized on more or less one single host, some species attack living ants, others also attack larger insects.
Since the traditional species (C.sinensis), which occurs only in the Himalayas, cannot come close to meeting the enormous worldwide demand, is now considered endangered, and is very difficult to bring to fruition, C.militaris, a close relative with similar potential, has been produced on an industrial scale in Asia for about 15 years.
Cordyceps militaris loses the ability to fruit particularly quickly, after no more than 1 year or 5 transfers to a new culture medium, it no longer gets beyond mycelial formation. In contrast to stander fungi (Basidiomycota), cultures of various tubular fungi (Ascomycota) cannot be kept fertile for a particularly long time by cloning. Therefore, new hybrids from ascospores have to be grown again and again for ongoing production.
-doping agent to increase performance
-against tumors & malignant tumor metastases
-antibiotic
-against colds
-stimulating the immune system
-infections
-sarcomas
This is attributed to the ingredient Cordycepin.
Cordyceps militaris contains anti-inflammatory polysaccharides, which are also effective against tumors and their metastases. The ingredient cordycepin kills bacteria. Furthermore, in traditional Chinese medicine it is said to have aphrodisiac and lung and kidney strengthening effects. The mushroom is also used in Asia as a medicine against colds and as a doping agent.
1. Growing
Growing Procedure
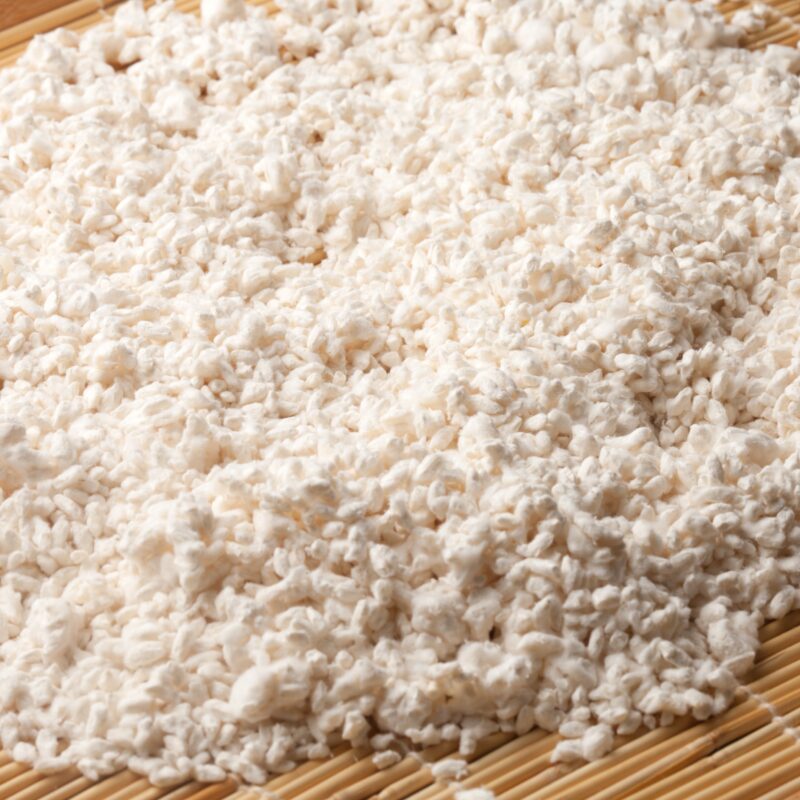
A common method is a technique of pouring a special broth of various ingredients over rice grains and then sterilizing this mix. Ideally, such cultures are inoculated with liquid broth. You need tall jars or microboxes with sterile filters. The fungus then hatches in the closed container, and the high CO² content does little harm to it. Advantages of the “in vitro” process are that Cordyceps militaris are later hygienically perfect, because no contamination can creep in and you do not need a classic fruiting room with complex climate control.In Asia, the remaining “substrate cake” is also harvested, dried and later ground. A special kind of chicken feed, the coveted cordycepic acid is later found in the eggs.
Substrate recipes with dried silkworms or chicken eggs can be found among successful breeders, as well as numerous recipes for making the nutrient broth with which you soak the rice. Malt extract, dextrose, nutritional yeast, tapioca starch, soyapeptone, gypsum and lime are the basis for such a broth, potato extracts and certain chemicals can be helpful whilst cultivating Cordyceps militaris.
Growing
Agar Culture Media: PDA/MEA with egg
Cropping:
Containers for fruiting: glass jars with filter port
Biological efficience:
Substrates: dead insects or rice with egg nutrition
PH: 5,6
Growing Characteristics
out of dead insect bodies
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp °C |
20-24 | 22(12h) +12(12h) | 22 |
Relative Humidity % |
80-90 | 70-90 | 90-95 |
Duration d |
7-21 | 7 | 15 |
CO2 ppm |
>10000 | 500 | 500 |
FAE per h |
0-1 | 8 | 8 |
Light lux |
– | 200(12h) | 500-1000 (12h) |
Affiliate Partner
Natural Habitat
Cordyceps militaris lives on dead pupae of various large butterflies, rarely also on caterpillars. Depending on the author, it is rare to quite common, widespread throughout the northern hemisphere, and produces fruiting bodies in Europe from August to November.
Meadows, parks, forests, on dead, buried or exposed insect larvae, later decomposers, usually not found in Europe, from summer to autumn, extremely rare.
2. Identification
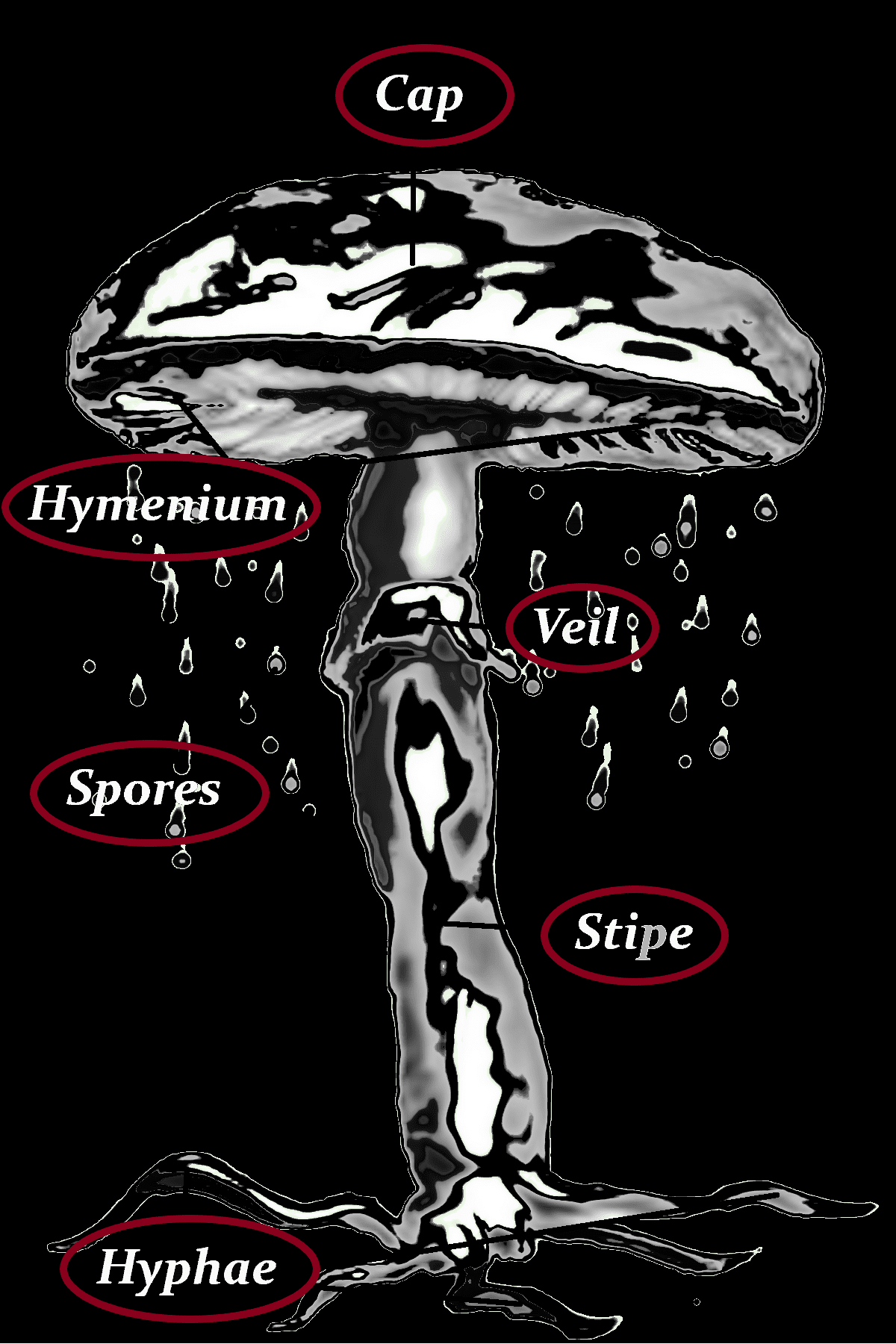
Cap
-< 1 cm Ø
-50 mm high
-yellow, yellow-orange, orange-red to brick-red
-tongue-shaped tip with orange-red warts
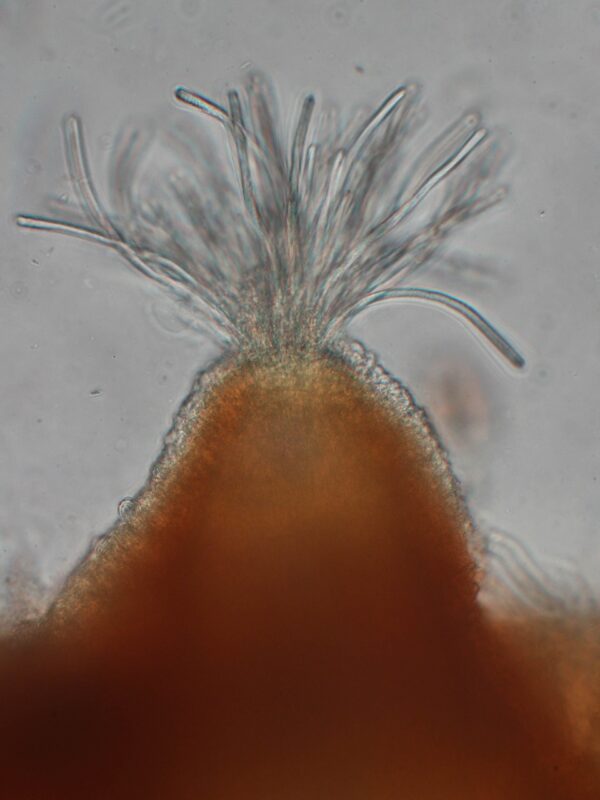
Hymenium
–
Spores
-white
-transparent
-4-6 x 1-2 µm
-cylindrical
-spindle-shaped
Stipe
-orange-red to brick-red
-they protrude almost seamlessly from the head
-often curved
-long
-thin
-rooted in the dead insect’s body
Hyphae
–
Danger of confusion
Ophiocordyceps sinensis, Typhula fistulosa, Ophiocordyceps sphecocephala
Veil
–
3. Consuming
Gourmet
Cordyceps militaris is a highly valued medicinal mushroom, despite to it neutral flavour.
Flesh
yellowish
Taste
neutral
Smell
neutral
Nutritional content
.
4. Data med, edible
other names
| Chinesisch (traditionell) | 北蟲草 |
| Chinesisch (traditionell) | 蛹蟲草 |
| Chinesisch (traditionell) | 黃金蟲草 |
| Dänisch |
Puppe-Snyltekølle
|
| Englisch |
Scarlet Caterpillar Club
|
| Estnisch |
harilik kedristõlvik
|
| Finnisch | punaloisikka |
| Französisch |
Cordyceps militaire
|
| Japanisch | サナギタケ |
| Japanisch | 蛹茸 |
| Litauisch |
Karingoji grūdmenė
|
| Niederländisch | Rupsendoder |
| Norwegisch | rød åmeklubbe |
| Russisch |
Кордицепс военный
|
| Schwedisch | röd larvklubba |
| Tschechisch |
housenice červená
|
| Wissenschaftl. Name |
Cordyceps militaris
|
other names
Lavaria gemmata, Xylaria militaris, Torrubia militaris, Corynesphaera militaris, Hypoxylon militare, Sphaeria militaris, Puppenkernkeule, Orangerote Puppenkernkeule
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division | Ascomycota |
| Class | Sordariomycetes |
| Order | Hypocreales |
| Family | Cordycipitaceae |
| Genus | Cordyceps |
| Species | C. militaris |
| Ecology | Parasitic |