Psilocybe subaeruginosa
Description
Psilocybe subaeruginosa is an integral part of the delicate dance of ecosystems, playing a vital role in the natural balance of our environment. Found predominantly in Australia and New Zealand, these mushrooms often emerge from forested areas, where they form symbiotic relationships with the roots of certain trees. Their underground interactions contribute to nutrient cycling, aiding in the health and vitality of the ecosystem they call home.
Lets uncover the secrets of Psilocybe subaeruginosa together, and let it guide you on a path of self-discovery, exploration, and awe-inspiring wonder. An subtle and earthy aroma fills the air, awakening your olfactory senses.

The genus Psilocybe is known for a number of hallucinogenic representatives. The baldhead genus is the most studied genus of hallucinogenic mushrooms.
Psilocybe subaeruginosa, known as the “Magic Mushroom Down Under,” holds a remarkable historical connection to the indigenous Maori people of New Zealand. For centuries, these ancient cultures revered and utilized this extraordinary fungus in their spiritual practices and ceremonies.
The Maori people considered it a taonga (a treasured possession) and a connection to their cultural heritage. The mushroom’s potent effects were respected and used responsibly, fostering a deep respect for nature and the spiritual realm
© Michael Wallace
Collection August 2024
Grab them, they are hot! 😊
Properties
Psilocybin was isolated from Psilocybe subaeruginosa at between 0.06% and 1.93% and psilocin up to 0.17%.
Psilocybe subaeruginosa contains psychoactive compounds such as psilocybin, psilocin, and baeocystin. These substances are known for their hallucinogenic effects, which can induce altered states of consciousness, visual distortions, and profound introspection.
Hallucinations
Psilocybe subaeruginosa can induce visual (especially withing high doses), auditory, and sensory hallucinations.
Euphoria and Introspection
Many report feelings of euphoria, introspection, and enhanced creativity.
Altered Perception
Users experience shifts in perception of time, space, and reality.
Mindset and Setting
The effects are influenced by mindset and environment.
Growing
How to Grow Psilocybe subaeruginosa?
Psilocybe subaeruginosa, a potent wood-loving mushroom similar to Psilocybe cyanescens and Psilocybe azurescens, is native to New Zealand (you may use the growing methods describe in their guides). Cultivating this species can be a fascinating and rewarding experience. Here is a step-by-step guide on how to grow Psilocybe subaeruginosa:
- Spore Inoculation: Begin by obtaining Psilocybe subaeruginosa spores from a reliable source. Prepare your growing materials, including sterilized jars, agar plates, and a pressure cooker. In a sterile environment, inoculate the spores onto agar plates or directly into sterilized jars filled with a suitable substrate. The substrate should be grain but can also consist of wood chips or cardboard which takes little longer to colonize.
- Incubation: Place the inoculated jars or agar plates in a clean, dark, and warm environment. Monitor the jars or plates for signs of mycelial growth, which should appear as white, thread-like strands spreading throughout the substrate.
- Colonization: Allow the mycelium to fully colonize the substrate. This process typically takes several weeks. Maintain proper humidity levels by misting the jars or plates occasionally. It’s crucial to prevent contamination during this stage, so maintain strict hygiene practices and avoid introducing foreign contaminants…
PH Levels
Agar Culture Media
5.0 – 6.0
Spawn Run
5.5 – 6.5
Fruiting Phase
5.5 – 6.5
Harvest
none
Any Sale Helps us Doing what we Love 😊
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp °C |
21-24°C (70-75°F) | 18-21°C (65-70°F) | 16-22°C (60-68°F) |
Relative Humidity % |
90-95 | 90-95 | 85-90 |
Duration d |
10-21 | 7-14 | 7-21 |
CO2 ppm |
>5000 | 800-1200 | <1000 |
FAE per h |
0-1 | 4-6 | 4-8 |
Light lux |
50-150 | 100-800 | 500-1000 |
How to Fruit Psilocybe subaeruginosa?
- Transferring to Bulk Substrate: Once the substrate is fully colonized, prepare a larger container for bulk substrate. Suitable options include a monotub or a large plastic container. Fill the container with a mixture of pasteurized wood chips, straw, and vermiculite. Transfer the colonized substrate from the jars or agar plates to the bulk substrate.
- Casing Layer: Apply a thin layer of moist sterilized soil or vermiculite on top of the bulk substrate as a casing layer. The casing layer helps retain moisture and promotes the formation of mushroom pins.
- Fruiting Conditions: Place the container in a controlled environment with optimal conditions for fruiting. Maintain high humidity levels by misting the casing layer regularly. Provide indirect light or natural daylight to initiate fruiting.
- Mushroom Development: With patience, small mushroom pins will begin to emerge from the casing layer. Continue to maintain proper humidity and temperature levels. As the mushrooms grow, adjust the misting to avoid waterlogging, which can lead to rot or contamination.
Harvest Psilocybe subaeruginosa
- Harvesting: When the mushroom caps have fully expanded and the veil underneath them begins to break, it is time to harvest. Use clean, sharp scissors or a sterile knife to cut the mushrooms at the base of the stem. Harvesting in stages as the mushrooms mature will ensure a continuous supply.
- Subsequent Flushes: Psilocybe subaeruginosa can produce multiple flushes of mushrooms. After each harvest, maintain proper environmental conditions and mist the casing layer to encourage the development of new pins. Repeat the process until the substrate’s nutrients are depleted, and the yield diminishes significantly.
Remember, growing Psilocybe subaeruginosa may be subject to legal restrictions in your location. Always adhere to the laws and regulations governing the cultivation and use of psychoactive substances.
Cropping Cycle
Inoculation Phase
Transfer mycelium from agar plates to sterilized grain spawn (e.g., rye, millet). This typically takes 2-4 weeks for the mycelium to fully colonize the grain.
Spawn Run
Transfer colonized grain spawn to a bulk substrate (e.g., a mix of pasteurized straw, manure, and/or coco coir). This phase can take 2-4 weeks.
Fruiting Phase
Transfer the colonized substrate to fruiting conditions (high humidity, fresh air exchange, light). Pinning usually occurs within 1-2 weeks, with mature mushrooms appearing in another 1-2 weeks.
Harvest
Typically, 1-2 weeks after pinning, mushrooms are ready for harvest. Usually we do 2-4 flushes.

How to make Agar Culture Media?
- Dissolve the malt extract and agar in distilled water.
- Sterilize the solution by autoclaving at 121°C for 15-20 minutes.
- Pour the sterilized media into petri dishes or other containers under sterile conditions.
- The Yeast is optional, but you can add it to any recipe for nutritions, same for Peptone.
Malt Yeast Peptone Agar
MYPA
Yeast Extract: 4g
Peptone: 5g
Agar: 15g
Distilled Water: 1L
Malt Extract Agar
MEA
Malt Yeast Agar
MYA
Potato Dextrose Yeast Agar
PDYA
Potato Infusion: 200g (from boiling 200g of diced potatoes in 1L of water, then straining)
Fruiting Containers
Trays
Open trays placed in a high-humidity chamber or tent.
Monotubs
Plastic storage bins with modified lids and holes for ventilation.
Martha Tents
Small greenhouse-style grow tents with shelves, often equipped with humidifiers and fans for optimal conditions.
Shotgun Chamber
Transparent plastic containers with drilled holes for ventilation and a dry agent at the bottom.
Substrate
Wood Debris
It grows from wood debris in Australian native forests and pine plantations.
Preferred Environment
It thrives among eucalyptus debris and clumps of grass.
Occasional Dung Growth
Although less common, it can also be observed growing on dung2.
Biological efficiencie
(BE): This measures the weight of fresh mushrooms harvested compared to the dry weight of the substrate. For Psilocybe subaeruginosa, BE can vary widely depending on growing conditions but generally ranges from 50% to 150%.
Example Calculation: If 1 kg of dry substrate yields 1.5 kg of fresh mushrooms, the BE is 150%
Sometimes we miss a piece
Identification
How to identify P. subaeruginosa
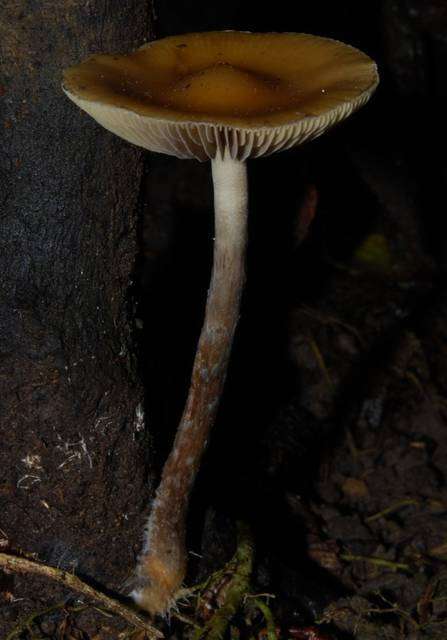
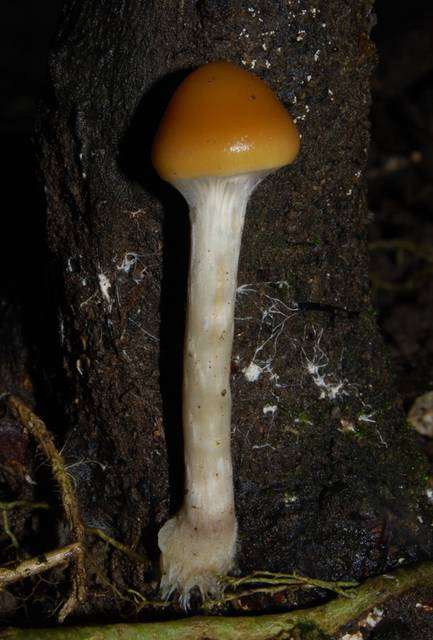
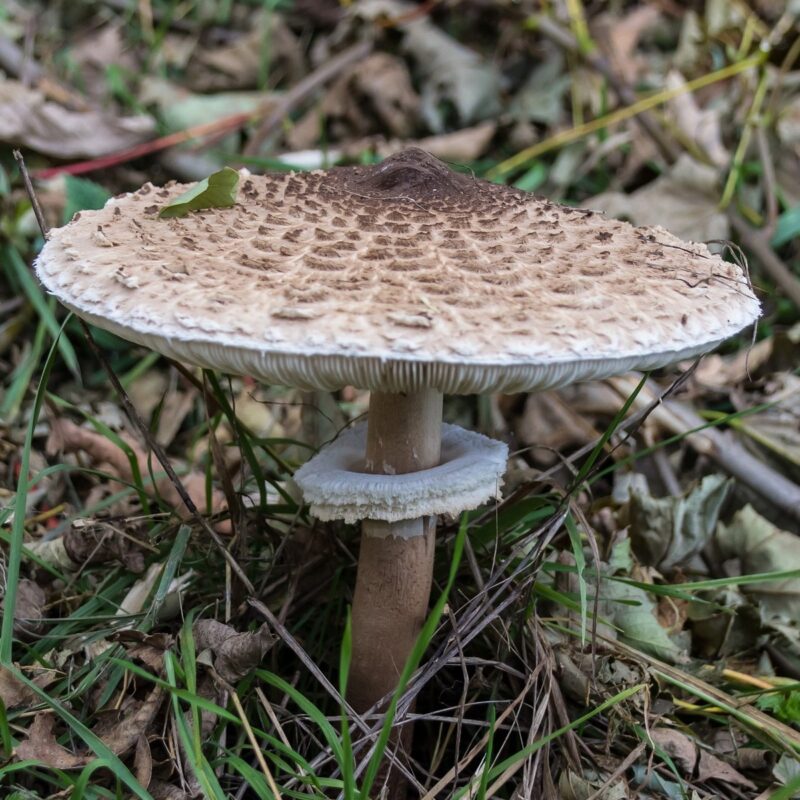
Its caramel-brown cap, often with a slight golden hue, distinguishes it. The convex cap grows between 1 to 6 centimeters in diameter, darkening as it dries. The stem (stipe) can reach up to 10 centimeters, slender but sometimes swollen at the base. Upon bruising, both cap and stem turn blue—the same color as its spore print
Cap
1-6 cm
conical to convex
cinnamon-brown
hygrophanous
margin moistly striped
rising with age
often with a slight hump
bluish bruises where damaged
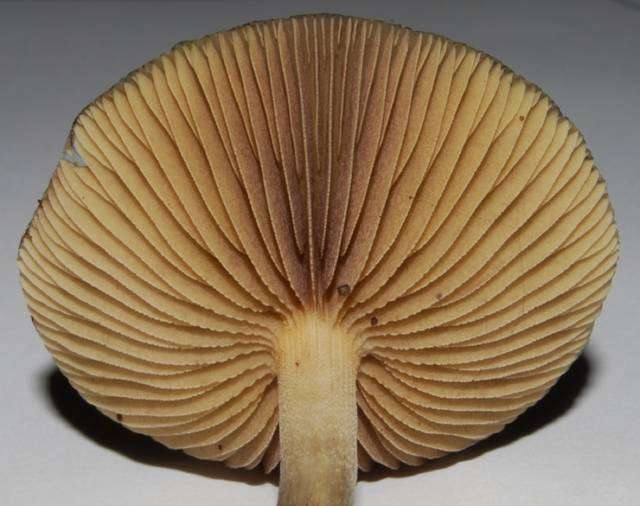
Hymenium
crowded
cream when young
purplish-brown when old
with adnate-to-annex binding
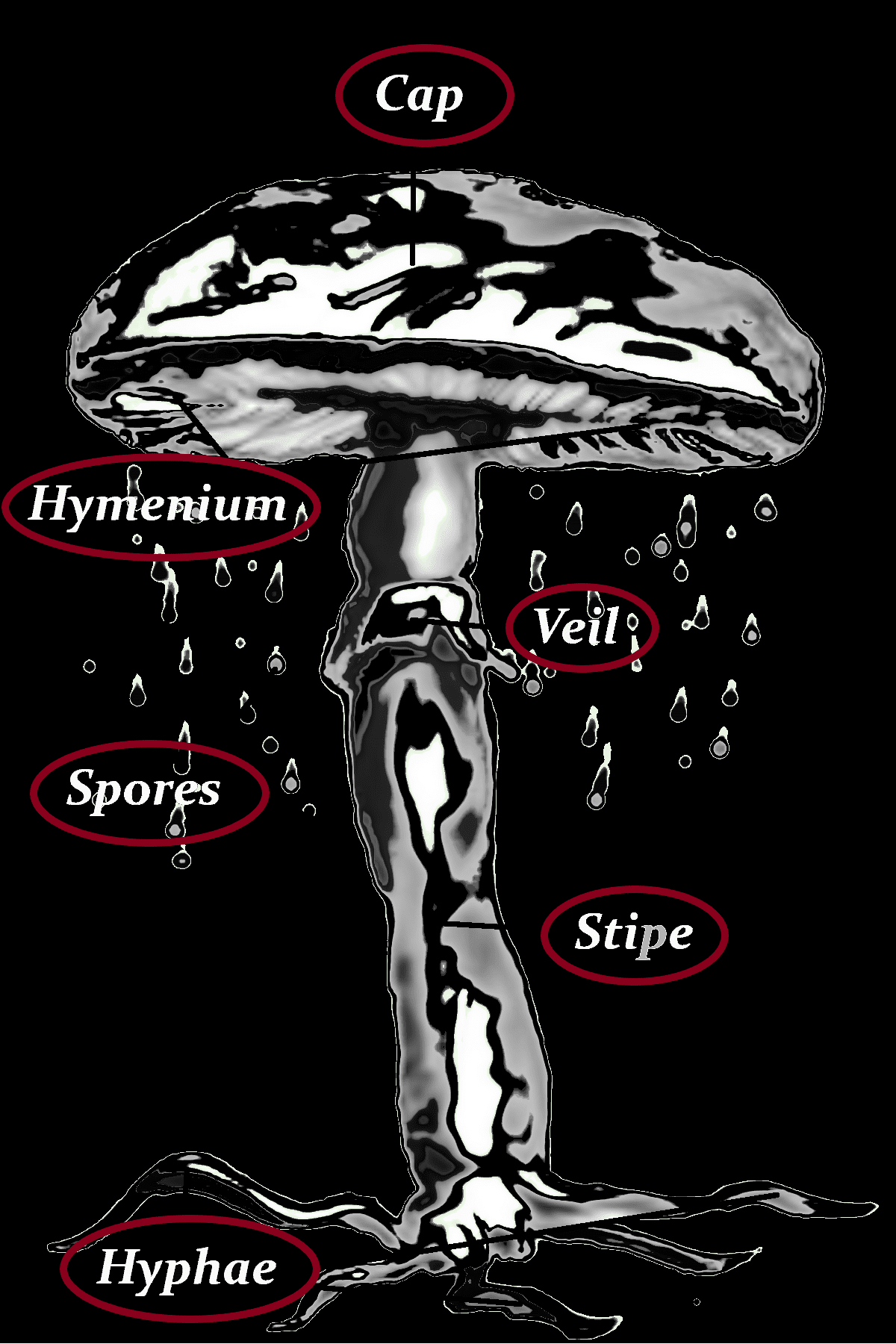
Stipe
4,5 to 12 cm long
0,2 to 0,4 cm thick
white to grey
finely striped
equal to slightly enlarged at the base
Veil
With a white curtain partial veil that soon disappears, often leaving traces on the upper trunk.
dark brown
drooping
grooved
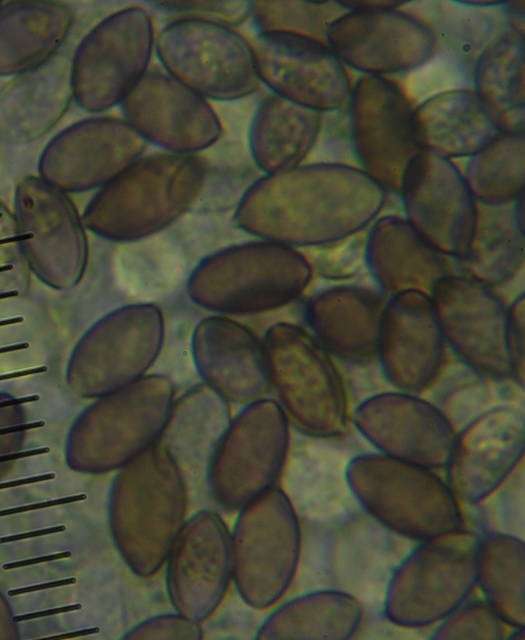
Spores
14 x 7 µm
dark purple-brown
subellipsoid
Danger of confusion
Galerina marginata, Galerina species, Hypholoma, Inocybe, Leratiomyces ceres, Coprinellus sect. Micacei, Pholiota communis, P. allennii, P. azuresecens, P. cyanescens, P. makarorae, Psilocybe subsecotioides, P. weraroa
Hyphae
branching
root-like strands
within the substrate
forming a network
absorbs nutrients
spreads the mycelium.
white to gray
Consuming
Dosis
Depending on the particular strain, growth method, and age at harvest of Psilocybe subaeruginosa, psilocybe mushrooms can come in rather different potencies. It is recommended to weigh the actual mushrooms, better then counting them. 10% of the mushrooms mass is left, when dried. Take a look at Properties, to find out how potent they are.
Typical:
There is an urgent warning against food experiments with Psilocybe subaeruginosa. Collecting, possessing and selling drug mushrooms is illegal in many countries around the world.
Here’s how to unlock the true root of Your Brain
– Without worrying about low quality ingredients
Effect
Due to the presumed main ingredient, psilocybin, the same effect can be expected as with other types of well-known hallucinogenic mushrooms. At this point, it is convenient to refer to the description of the effects of Psilocybe cumbensis.
Sensory Perception
Mild Taste: P. subaeruginosa has a mild flavor, often reminiscent of nuts or other mushrooms.
P. subaeruginosa contains psilocybin, which induces altered states of consciousness, visual distortions, and introspection.
Smell
The smell can be earthy, mealy, mossy, or slightly sweet.
Some describe a characteristic mushroom odor
Taste
The taste is often mild, reminiscent of nuts or mushrooms.
Chewing may intensify the flavors.
Flesh
The mushroom’s flesh is tender and breaks easily.
It can range from creamy white to light brown.
Composition
Psilocybe subaeruginosa, like other Psilocybe species, contains a variety of bioactive compounds, primarily psilocybin and psilocin, responsible for its psychoactive effects. The presence of other compounds such as baeocystin, norbaeocystin, and beta-carbolines may also contribute to its overall pharmacological profile. Additionally, these mushrooms offer some nutritional benefits, including proteins, vitamins, and minerals.
The exact concentrations of these compounds can vary based on factors such as growing conditions, substrate composition, and mushroom maturity. Further research is needed to fully understand the pharmacology and potential health benefits of Psilocybe subaeruginosa.
Psilocybin Content
P. subaeruginosa contains psilocybin, the primary psychoactive compound responsible for its hallucinogenic effects.
Experts consider it one of the most potent species, with up to 1.93% psilocybin when dried.
Besides psilocybin, P. subaeruginosa contains other psychedelic-promoting alkaloids:
Psilocybin
Chemical Structure: 4-phosphoryloxy-N,N-dimethyltryptamine
Role: Primary psychoactive compound. Psilocybin is metabolized in the body to psilocin, which then acts on serotonin receptors in the brain, particularly the 5-HT2A receptor, leading to altered perceptions, mood, and consciousness.
Baeocystin
Chemical Structure: 4-phosphoryloxy-N-methyltryptamine
Role: A minor analog of psilocybin, also psychoactive. Its effects are not as well-studied but it is believed to contribute to the overall psychoactive experience.
Norbaeocystin
Chemical Structure: 4-phosphoryloxytryptamine
Role: Another minor compound with potential psychoactive properties. Its effects are less understood compared to psilocybin and psilocin.
Other Alkaloids
Ergosterol
A sterol present in fungal cell membranes, similar to cholesterol in animals. Ergosterol is a precursor to vitamin D2 when exposed to UV light.
Polysaccharides
Contribute to the structural integrity of fungal cell walls. Some polysaccharides from fungi have immunomodulating properties.
MAOIs
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors that enhance psychedelic experiences
Beta-Carbolines
Examples: Harmane, norharmane
These compounds act as monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), potentially enhancing and prolonging the effects of psilocybin and psilocin by inhibiting their breakdown in the body.
Proteins
Proteins
Content: Mushrooms typically contain a moderate amount of protein, including essential amino acids.
Vitamins
Examples: B-vitamins (B2, B3, B5, B7), Vitamin D2 (ergocalciferol)
Role: Essential for various metabolic processes. Vitamin D2 is particularly noteworthy as it is converted from ergosterol upon exposure to sunlight.
Minerals
Examples: Potassium, phosphorus, selenium, copper
Role: Essential for numerous biological functions, including enzyme activity, bone health, and antioxidant defense.
Phenolic Compounds
These may have antioxidant properties, contributing to the overall health benefits of consuming mushrooms.
Lipids
Fungi contain various lipids essential for cell membrane structure and function.
other names
P. subs, P.s. Cleland, Psilocybe australiana, P. eucalypta
Taxonomical Hierarchy
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division | Basidiomycota |
| Class | Agaricomycetes |
| Order | Agaricales |
| Family | Hymenogastraceae |
| Genus | Psilocybe |
| Species | P. subaeruginosa |
| Ecology | saprotrophic |
Any Sale Helps us Doing what we Love 😊