Description
Properties
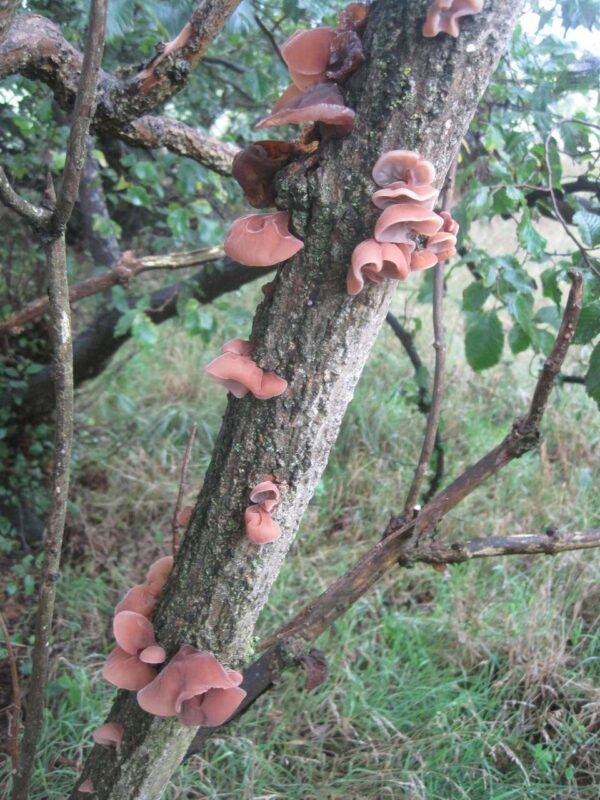
Judas ear (Auricularia auricula-judae, Syn.: A. auricula, A. sambucina, Hirneola auricula-judae) is a fungus with almost worldwide distribution. A similar species with an East Asian distribution (A. polytricha) is called Mu-Err (Chinese 木耳, pinyin mù’ěr – “wood ear, tree ear”), Black Fungus, elder fungus or sponge, ear lobe fungus, or cloud ear fungus (雲耳 / 云耳, yún’ěr – “cloud ear”), which is used in many dishes of Asian cuisine and especially Chinese cuisine.
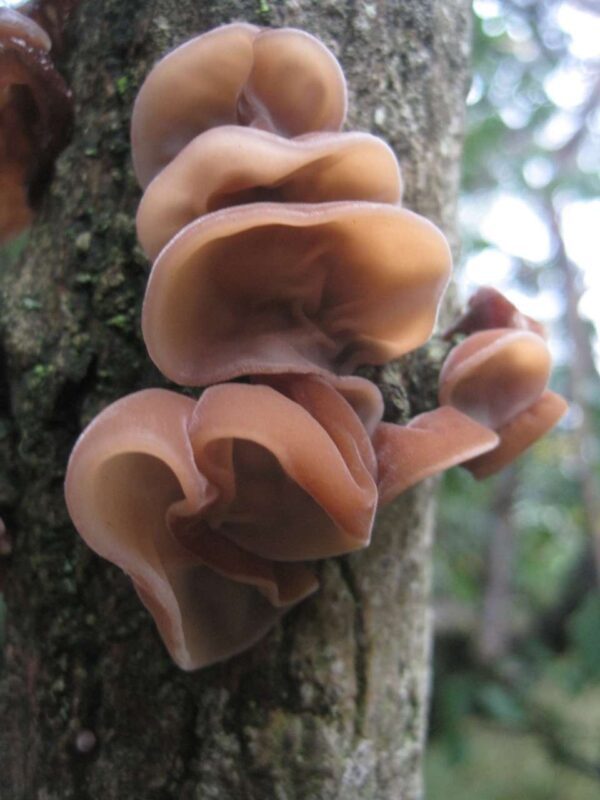
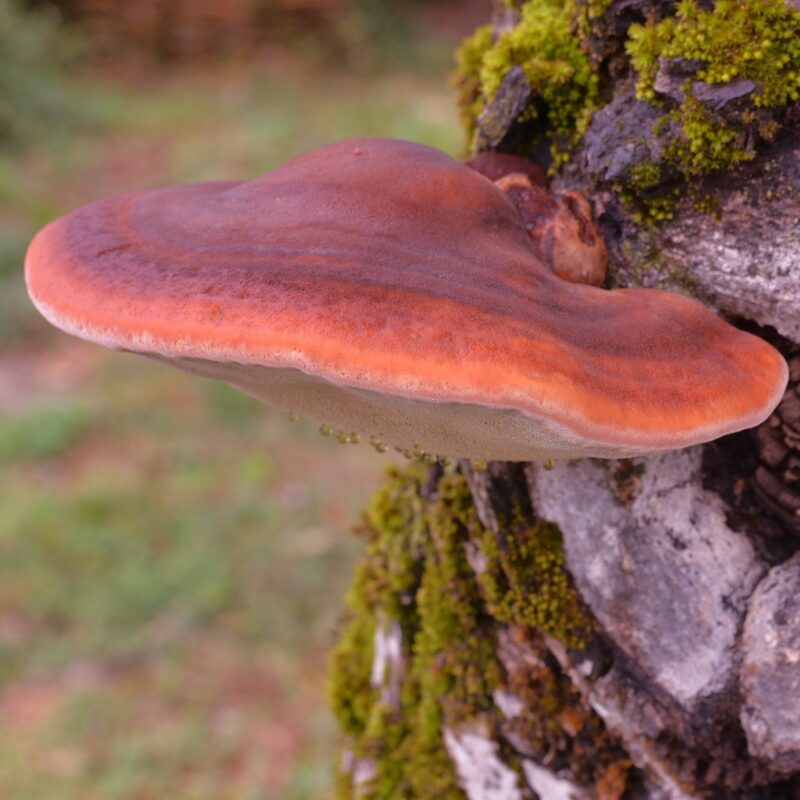
This mushroom is one that is very distinct from most others that I have seen. To begin with, the most striking feature is the ear shape it possesses. It has a jelly-like texture, and it is soft to the touch when fresh but hard when it is dry. Aside from that, it has a red-brown color which varies depending on the age of the mushroom. When it gets older, the color tends to be more black. The best part of this mushroom is that it is edible and has comfounds within its cell wall that have been researched to find medicinal contributions. Anti-cancer research is one that is conducted on this mushroom just like with the sea cucumber. Now, don’t let me give it all away. Please keep reading the other pages to learn about the many aspects of this mushroom. Learn about the relationships to other organisms, the reproduction and life cycle, and so much more!
Hakeke or NZ wood ear mushrooms (Auricularia novozealandica formerly known as Auricularia cornea) are a unique mushroom which have been eaten as a food in New Zealand for hundreds of years. Close relatives of these fungi are also prized overseas, particularly in Asia, and at one point in time a thriving industry existed based on the export of wild New Zealand wood ear mushrooms to China.
To continue, this fungus is one of the known fungi that is able to develop in and withstand in freezing temperatures (Paassen, 2010.) It can freeze solidly and thaw out, and still it would not have any problems. This is very useful since it is able to grow most time especially during the coldest month of the year, January.
Yuan(1998) demonstrated that Wood Ear’s water-soluble polysaccharide fraction has a hypoglycemic effect on genetically diabetic mice. A water insoluble glucan similar to β 1-3 D-glucans and β 1-6 D-glucans (560,000-610.00 bp) was isolated from the hot water extract of the fruiting bodies. In vitro tests have shown strong antitumor activity against the solid form of Sarcoma 180 Kio(1991).
Wound pain, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, inflammation, blood clotting disorders, thrombosis, vascular problems, heart attack prevention, circulatory disorders, regulation of blood lipid levels.
Support for problems in the gastrointestinal area, lungs, liver, throat, cramps, numbness and injuries, regulator for increased vaginal discharge, hydrates the lungs, has a relaxing effect.
In Chinese medicine, mushrooms are used in patients suffering from arteriosclerosis to improve the flow of blood and thus treat circulatory problems. They also have anti-inflammatory effects and lower cholesterol levels.
In commerce, Judas ears are usually available dried and are imported in large quantities, especially from Vietnam. They are rich in iron, potassium and magnesium and contain phosphorus, silicon and vitamin B1. In Chinese cuisine, fresh or rehydrated and freed from the stalk are used. When swelling, they reach many times their size in the dry state. They have only a slight, mushroom-like inherent flavor, but a special mouthfeel: a peculiar texture reminiscent of fresh seaweed. In addition, the Judas ear absorbs very well the flavors of the liquids in which it is prepared.

© Gihan Soliman
1. Growing
Affiliate Partner
Growing Procedure
Auricularia auricula-judae performs well in New Zealand conditions and is equally as happy on logs outdoors as it is on indoor sawdust / woodchip blocks. One kilogram of spawn is enough to inoculate approximately four sawdust or woodchip blocks (advanced method).
Growing
Agar Culture Media: MYA, MYPA, PDA, PDYA, DFA
Cropping Cycle: Every two to three weeks, 3-5 flushes
Containers for fruiting: Polypropylene bags and bottles. Each should be punctured with ten to twenty holes after full colonization (25 to 40 days after inoculation) to localize primordia formation.
Biological efficiencies: 20%
Substrates: Millet, milo, rye, wheat, or sorghum all support the formation of a vigorous and luxuriant mycelial mat. Rye Berries, Supplemented Sawdust,Logs
Growing Characteristics
-species hard to seperate
-parasitic and/or decomposing
-causes white rot
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp °C |
24-30 | 12-20 | 21-30 |
Relative Humidity % |
90-95 | 90-95 | 85-90 |
Duration d |
25-40 | 5-10 | 5-7 |
CO2 ppm |
5000-20000 | 600-1000 | 2000-5000 |
FAE per h |
0-1 | 5-8 | 4-5 |
Light lux |
– | 500-1000 | 500-1000 |
Natural Habitat
Auricularia auricula-judae is a weakling parasite on living trees or feeds saprobiotically on already dead wood; it is a white rot pathogen. Judas ear grows on numerous tree species, including birch, black locust, elm, walnut, mango, kapok, and most commonly, elderberry trees. Very rarely, the fungus is also found on conifers such as spruce (Picea). You can find the Judas ear almost throughout the year in suitable places. Since they are frost resistant, they can be dug out from under the snow even in the deepest winter. Judas ear is widespread throughout Europe.
-likes conifer wood/stumps, also elder, birch, willows, oaks, locust, mulberry, locust-acacia and other broadleaf trees.
-it is found where the soil is rich in wood debris
-prefers damp weather conditions, frost resistant, favors cool weather and grows throughout the temperate forests of the world
2. Identification
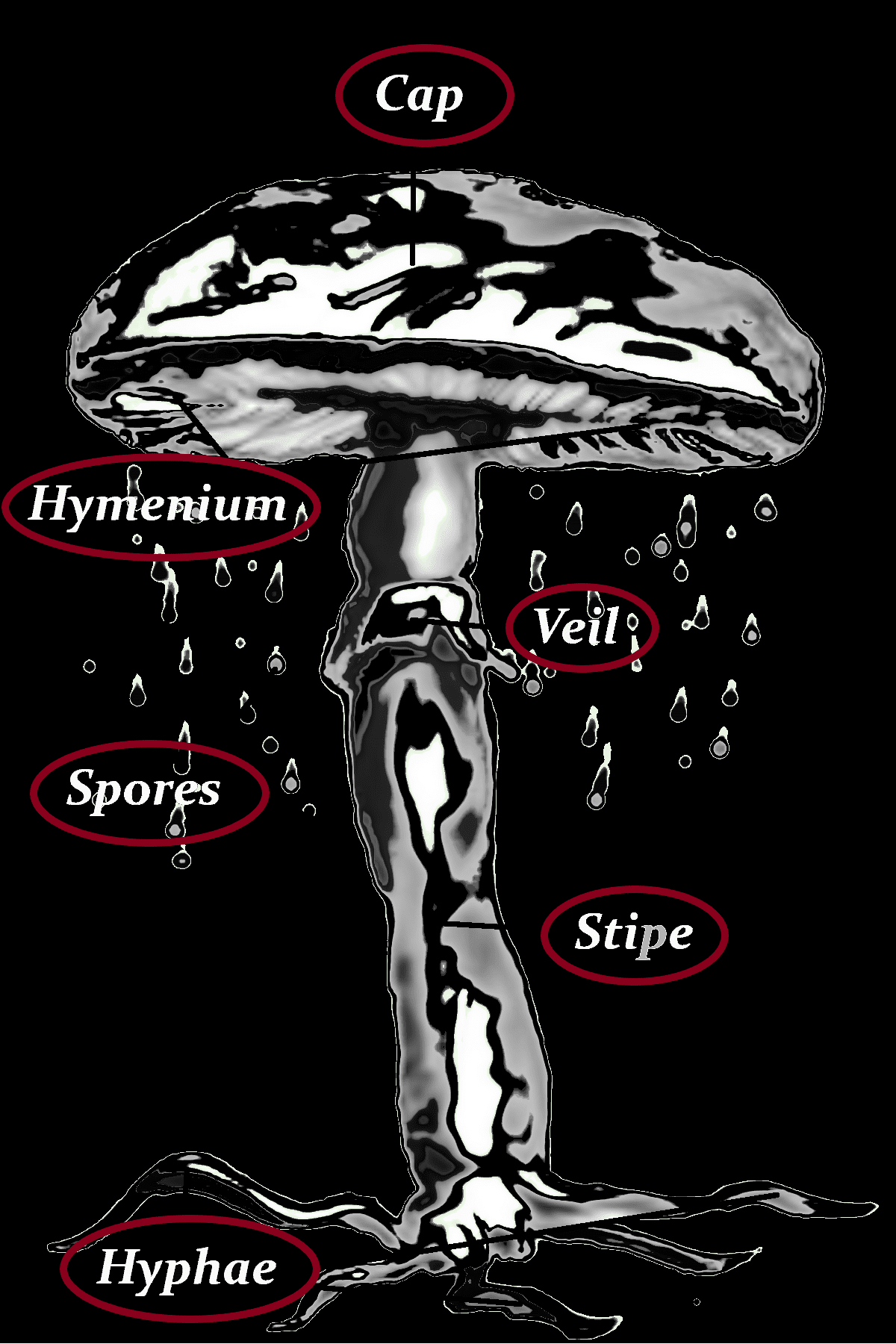
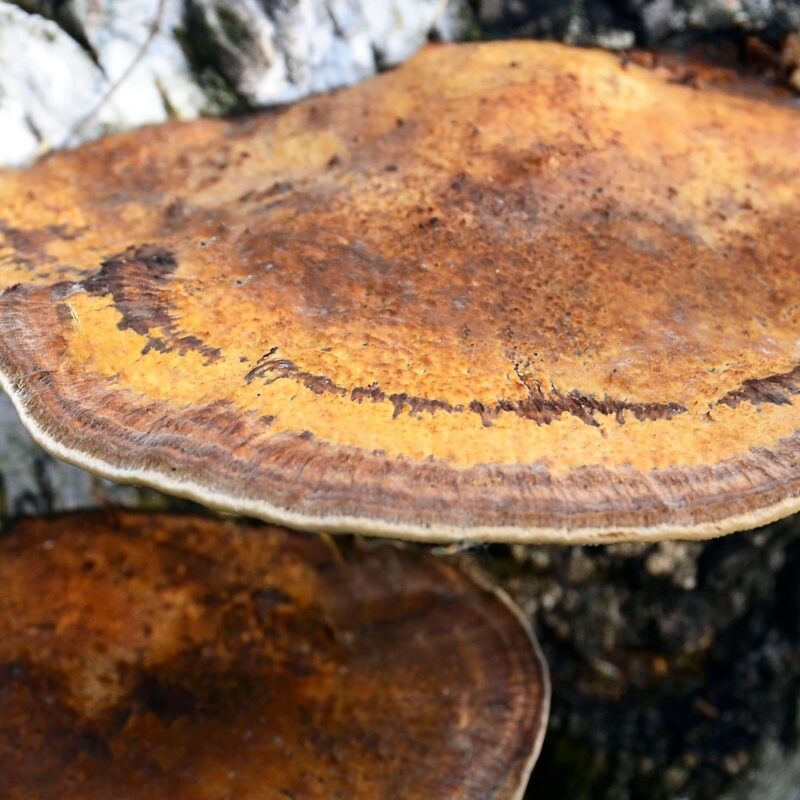
Cap
-2-15 cm Ø
-wrinkled in the center and upturned towards edge
-purple-reddish brown
-ear shaped
-a medulla of fine white hairs covers one side
-other side smooth
Hyphae
-longitudinally linear
-gets thicker with age and forms a dense cottony white mycelial mat
-gets blotchy in age with a greyish to brown discoloration
Stipe
–
Hymenium
-hairy surface produce the spores
Spores
-white after drop otherwise clear
-cylindrical, to sausage shaped
-11-14 x 4-6 μm
-basidia 4-spored
-clamp connections present
Danger of confusion
Schizophyllum amplum, Exidia recisa, Phaeotremella foliacea, Phaeotremella fimbriata, Cyphella digitalis, Auricularia mesenterica, Tarzetta cupularis, Tarzetta cupularis
Veil
–
3. Consuming
Gourmet
Auricularia auricula-judae is a relatively tasteless edible mushroom and can be used in soups or in mushroom dishes as a “stuffing” mushroom. These mushrooms are great sliced up in any asian style cuisine ranging from stir frys, soups, broths, hot pot, dumplings and so on. They add an interesting crunchy texture and mild but refreshing flavour to the dish.
Smell
unpleasant, musty, reminiscent of raw compost
Taste
jelly, mild, tasteless
Flesh
gelatinous in texture, fast rehydrated in water to natural form
Nutritional content
| 8–10% | protein |
| 0.8–1.2% | fat |
| 84–87% | carbohydrates |
| 9–14% | fiber |
| 4–7% | ash |
| 90% | Moisture content |
4. Data
other names
| Bunun (Taiwan) | kulkulaz |
| Chinesisch (traditionell) | 木耳 |
| Chinesisch (vereinfacht) | 黑木耳 |
| Deutsch | Judasohr |
| Dänisch | Almindelig judasøre |
| Englisch | Jelly Ear |
| Französisch | Oreille de Judas |
| Französisch | Oreille du diable |
| Hebräisch | אזנונית יהודה |
| Indonesisch | Lember |
| Japanisch | キクラゲ |
| Katalanisch | Orella de Judes |
| Litauisch | Tikrasis Ausiagrybis |
| Niederländisch | echt judasoor |
| Norwegisch | judasøre |
| Polnisch | Uszak Bzowy |
| Portugiesisch | Orelha-de-judas |
| Russisch | Аурикулярия уховидная |
| Schwedisch | Judasöra |
| Slowakisch | Uchovec bazový |
| Spanisch | Oreja de Judas |
| Tschechisch | ucho Jidášovo |
| Türkisch | kulak mantarı |
| Ukrainisch | Аурикулярія вухоподібна |
| Ungarisch | Júdásfülgomba |
| Wissenschaftl. Name | Auricularia auricula |
| Wissenschaftl. Name | Auricularia auricula-judae |
| Wissenschaftl. Name | Hirneola auricula-judae |
| Wissenschaftl. Name | Hirneola auricula-judae lactea |
other names
Auricularia auricula, Auricularia lacteal, Auricularia auricularis, Hirneola auricularis, Hirneola auricula-judae, Tremella auricula, Peziza auricula, Merulius auricula, Tremella auricula-judae, Peziza auricula-judae, Tremella auricula-judae var. caraganae, Tremella caraganae, Gyraria auricularis, Exidia auricula-judae, Auricularia sambuci, Hirneola auricula-judae, Hirneola auricula, Wood Ear, Ear Fungus, Tree Ear, Yu er, Mu-er, Mo-er, Maomuer, Yung Ngo, Muk Ngo, Kikiurage, Tree Jelly Fish, Mokurage, Aragekikurage, Black Fungus, Holunderpilz, Holunderschwamm, Ohrlappenpilz, Wolkenohrenpilz
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division Basidiomycota Class Agaricomycetes Order Auriculariales Family Auriculariaceae Genus Auricularia Species A. auricula-judae Ecology Saprotrophic |