© Joula (Bohemican)
Description
Properties
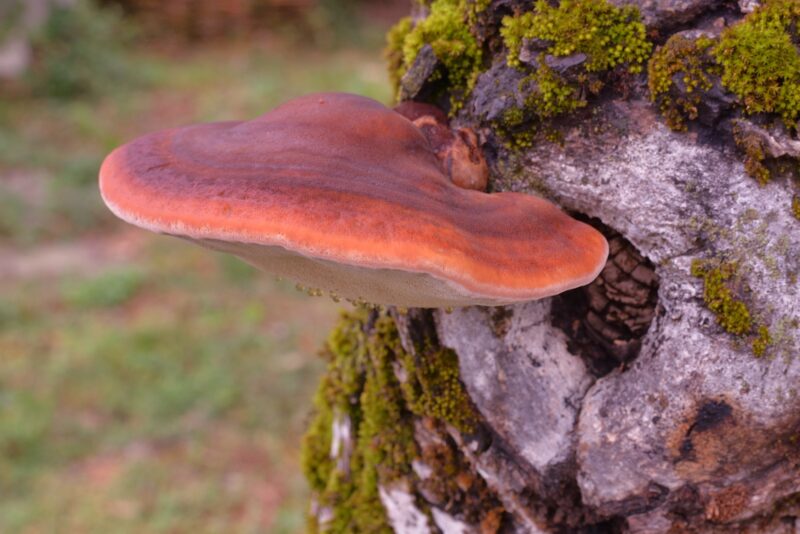
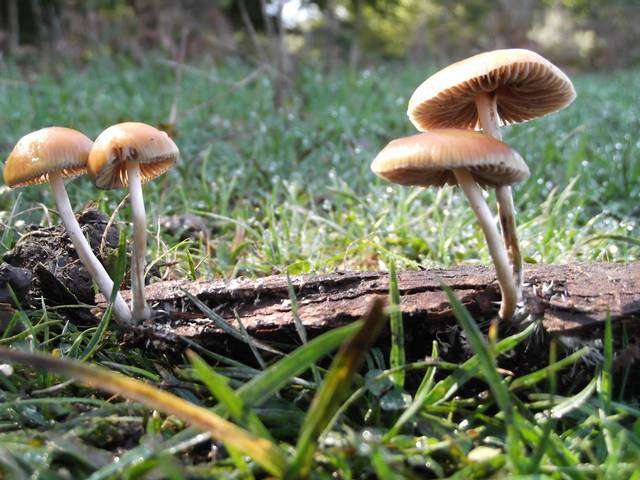
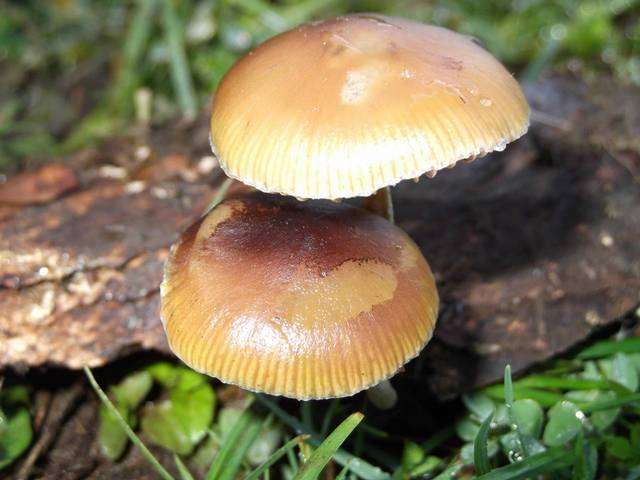
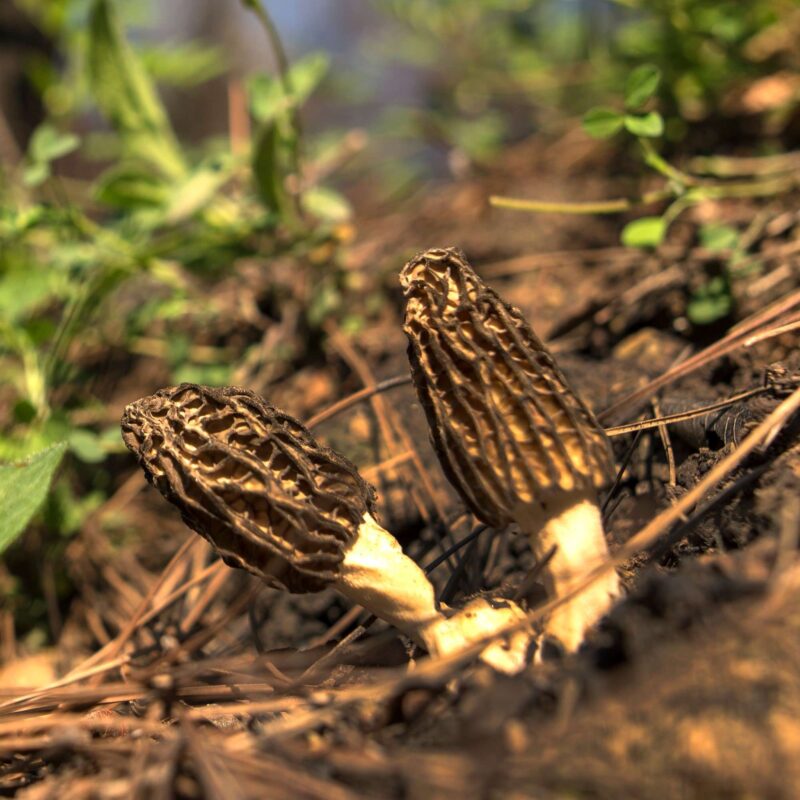
Psilocybe serbica is a species of mushroom known for its psychoactive properties and is a member of the Psilocybe genus. It is commonly referred to as the Serbian mushroom due to its discovery and prevalence in Serbia and neighboring regions.
Psilocybe serbica and other psilocybin-containing mushrooms have a long history of traditional use and cultural significance in certain regions, but the consumption of psychoactive mushrooms can have potential risks. It’s advisable to educate oneself about the risks, legality, and responsible use of such substances. Identifying it is only possible with certainty under the microscope.
The fruiting bodies if Psilocybe serbica grow on decaying wood & on wood chips used in horticulture. It is closely related to Psilocybe cyanescens, although the latter has a strong floury odor and taste and does not have translucent streaks when wet.
Psilocybe serbica, clearly hallucinogenic, is also one of the problematic species in terms of its botanical classification.
Psilocybe serbica has a hallucinogenic effect! The psilocybin content range from 0.11% to 1.34% dry weight. Baeocystin and psilocybin concentrations were highest in mushroom caps.
Psilocybe serbica contains various psychoactive compounds, including psilocybin, psilocin, and baeocystin. These compounds are responsible for the hallucinogenic effects commonly associated with consuming mushrooms of this species.
This awe-inspiring fungus boasts a rich cultural history intertwined with mystical experiences, making it a beloved and respected entity in the realm of entheogens.
This mystical mushroom has been used for centuries by indigenous communities, shamans, and spiritual seekers as a tool for healing, divination, and expanding consciousness. Its profound influence on art, music, and philosophy testifies to its enduring legacy throughout history.

© jonasgruska
1. Growing
Growing Procedure
Psilocybe serbica, a little known mushroom native to Europe, can be cultivated using the following steps:
Step 1: Preparing the Substrate
- Mix 2 parts vermiculite, 2 parts brown rice flour, and 1 part water in a large bowl.
- Fill wide-mouth glass jars with the substrate mixture, leaving about 3 cm (1 inch) of space at the top.
- Cover the jars with tin foil to prevent water from getting in.
- Sterilize the jars in a pressure cooker or Instant Pot for 30 minutes to kill any competing organisms.
- Allow the jars to cool down before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2: Inoculation
- Clean the area where you’ll be working with isopropyl alcohol to maintain sterility.
- Using a sterilized spore syringe, inject approximately 2 CCs of spore solution into each jar.
- Seal the jars and cover the top with tin foil.
- Repeat this process for each jar, ensuring cleanliness between each inoculation.
Step 3: Incubation
- Set up an incubator to create ideal conditions for the spawn run.
- Place the inoculated jars in the incubator, or if you have a suitable dark and warm spot in your house, use that instead.
- Check the jars every few days for signs of contamination and monitor the growth of white mycelium.
Step 4: Fruiting
- Once the jars are fully colonized with white mycelium, it’s time to initiate fruiting.
- Create a fruiting chamber by using a clear container that allows some airflow and maintains high humidity (>80%).
- Place the colonized jars inside the fruiting chamber and provide low levels of indirect light.
- Maintain fruiting parameter
- Spray the substrate with filtered or distilled water to keep it moist.
- Over time, mushrooms will start to grow from the colonized substrate.
- Harvest the mushrooms when they reach the desired size and maturity.
It’s important to prioritize safety and legality when engaging in any cultivation activities. Ensure you comply with local laws and regulations regarding the cultivation and use of psilocybin-containing mushrooms.
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp °C |
21°C-24°C (70°F-75°F) | 18°C-23°C (64°F-73°F) | 15°C-20°C (59°F-68°F) |
Relative Humidity % |
90-95 | 85-90 | 80-85 |
Duration d |
7-21 | 7-14 | 7-21 |
CO2 ppm |
>5000 | 1000-2000 | <1000 |
FAE per h |
0-1 | 4-6 | 4-8 |
Light lux |
– | 100-800 | 500-1000 |
Affiliate Partner
Growing
Agar Culture Media: MEA, MYPA, MYA, PDYA
Cropping Cycle:
Containers for fruiting:
Biological efficiencies:
Substrates:
Growing Characteristics
Natural Habitat
Summer to fall
Deciduous forests, spruce forests, forest meadows, rare in Western and Central Europe, from September to December.
Psilocybe serbica grows mainly in clumps, on well-decomposed conifers and deciduous trees, and together with Urtica spp. or rubus spp. on twigs, compost, plant debris, in woods, especially in moist places along streams, forest paths, and roadsides. It has not been reported to be synanthropic.
Preferred substrates are hardwood mulch made from oak, eucalyptus, Douglas fir, and alder. Fruiting occurs in cool weather, generally late September through January. The species can be easily grown on agar, grain seed, and cellulosic material, including wood chips and sawdust.
2. Identification
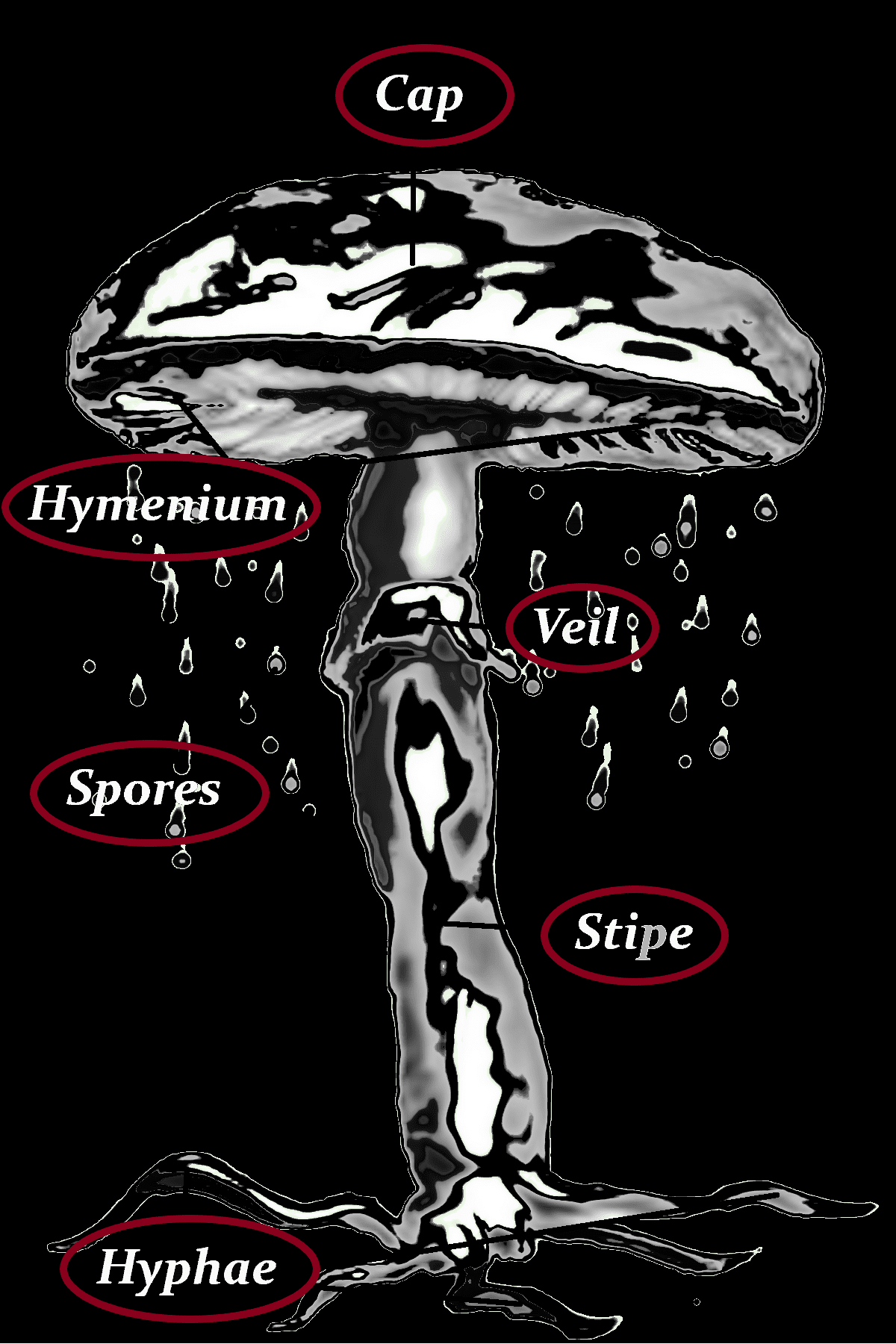
Cap
-1-2 (3) cm
-grayish brown, light brown
-hygrophanous
-sometimes slightly ridged often darker brown
-hemispherical
-possibly slightly humped
-never upturned
-bluish when injured
Stipe
-light brownish
-white-fibrous-floccose
-darker brownish to base
-very long
-base with mycelium white-felted
Hyphae
Hymenium
-gray, gray-brown, dark brown
-with intermediate lamellae
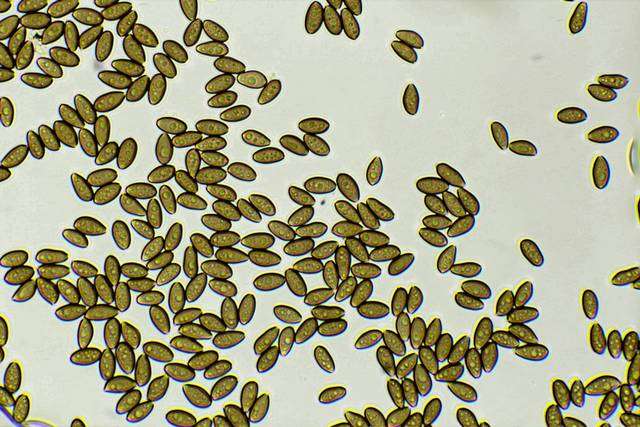
Spores
3-4 x 9-11 µm
-blackish brown
Danger of confusion
PSILOCYBE CYANESCENS, PANAEOLUS CYANESCENS, PSILOCYBE SEMILANCEATA, PROTOSTROPHARIA SEMIGLOBATA, PANAEOLUS PAPILIONACEUS, PANAEOLUS GUTTULATUS, PANAEOLUS FIMICOLA
Veil
-dark brow
-drooping
-grooved
3. Consuming
Dosis
There is an urgent warning against food experiments with Psilocybe serbica. Collecting, possessing and selling drug mushrooms is illegal in many countries around the world.
Depending on the particular strain, growth method, and age at harvest, psilocybe mushrooms can come in rather different potencies. It is recommended to weigh the actual mushrooms, better then counting them. 10% of the mushrooms mass is left, when dried. Take a look at Properties, to find out how potent they are.
Effect
Due to the presumed main ingredient, psilocybin, the same effect can be expected as with other types of well-known hallucinogenic mushrooms. At this point, it is convenient to refer to the description of the effects of Psilocybe cumbensis.
Duration:
5-6 hours
Smell
-neutral
-musty
Taste
-mild
Flesh
-brownish
-bluish
Composition
It is the hallucinogenic tryptamine contained in this type of mushroom called psilocybin.
4. Data
other names
Psilocybe bohemica, Böhmischer Kahlkopf,Psilocybe serbica f. sternberkiana (Borov.) Borov., Oborník & Noordel, Psilocybe bohemica Sebek 1983, Serbischer Kahlkopf
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division | Basidiomycota |
| Class | Agaricomycetes |
| Order | Agaricales |
| Family | Hymenogastraceae |
| Genus | Psilocybe |
| Species | P. serbica |
| Ecology | saprotrophic |