© Caleb Brown
Description
Properties
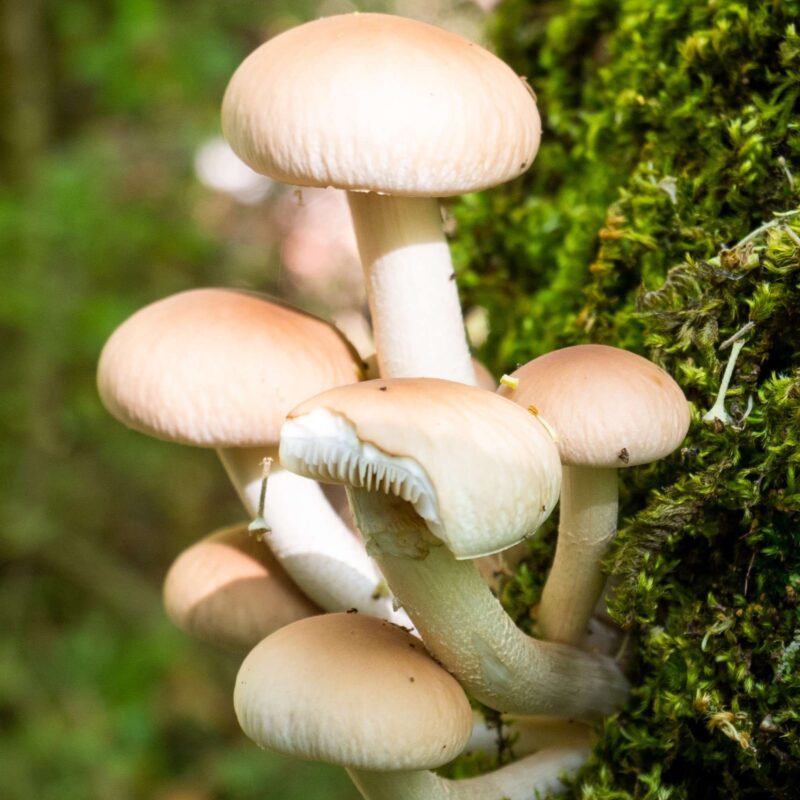
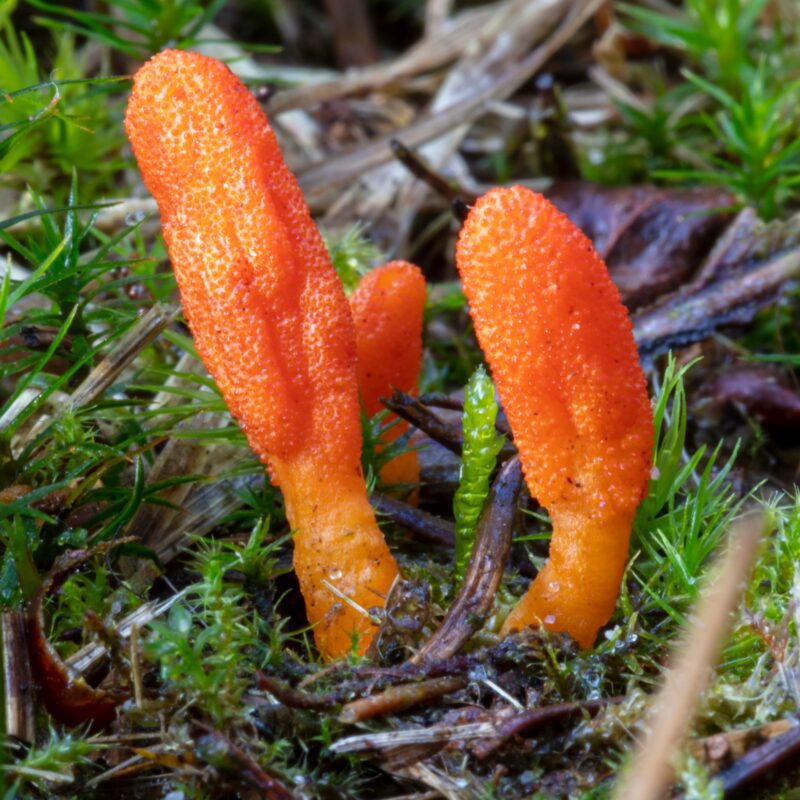
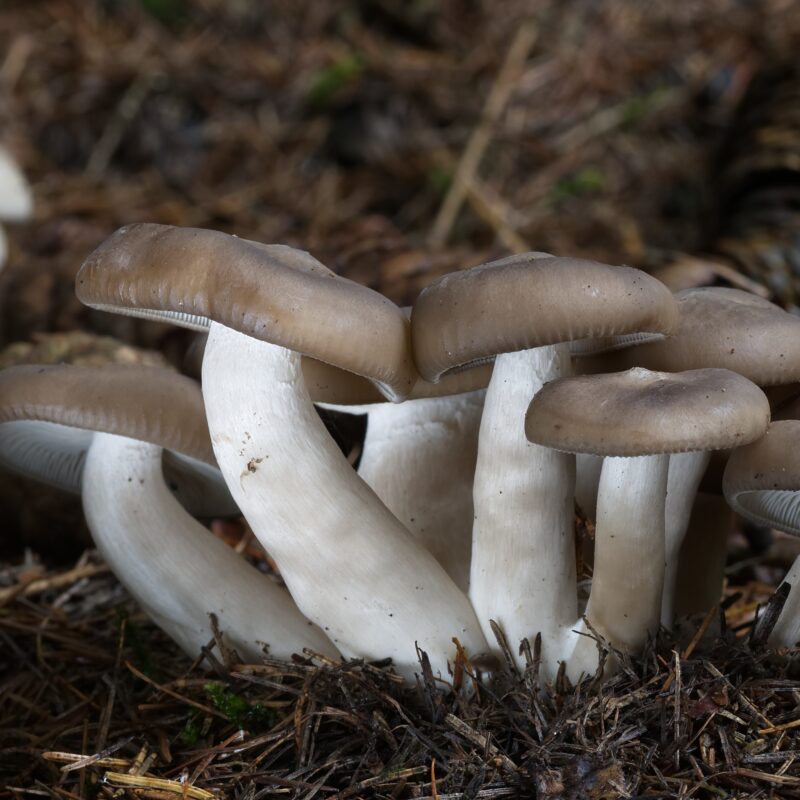
Psilocybe cyanescens, commonly known as the “Wavy Caps,” is a species of psychedelic mushroom belonging to the genus Psilocybe. It is widely recognized for its potent hallucinogenic properties and is highly sought after by individuals interested in the effects of psychedelic substances.
Please note that the cultivation, possession, or consumption of Psilocybe cyanescens and other psychedelic mushrooms may be illegal in many jurisdictions. It’s important to respect the laws and regulations of your country or region regarding the use of such substances.
Psilocybe cyanescens is eaten fresh or dried. These mushrooms, which grow on cow, buffalo or horse dung, grow in Java and Bali during the rainy season. The center of mushroom consumption in Java is the area around Yogyakarta, the Sultan’s ancient city near Borodur. The sacrificial bundles of the temple districts are adorned with mushroom sculptures. One way or another, tie-dye artists eat these magic mushrooms to get inspiration for their work and to see visions.
The Wavy Cap has a strong hallucinogenic effect. The psilocybin content can reach up to 2% of the dry matter. The latency period of this fungus ranges from 15 minutes to 4 hours.
Psilocybe cyanescens contains various psychoactive compounds, including psilocybin, psilocin, and baeocystin. These substances are responsible for the hallucinogenic effects when consumed.
When ingested, Psilocybe cyanescens can induce altered states of consciousness, sensory distortion, and profound visual hallucinations. The effects can vary in intensity and duration, depending on factors such as dosage, individual sensitivity, and set and setting.
-Red-brown discoloration on contact with potassium hydroxide solution (KOH)
-Dark brown with sodium hydroxide solution (NaOH)
-With iron sulfate (FeSO4) light brown to light yellow-brown
-No staining with phenol
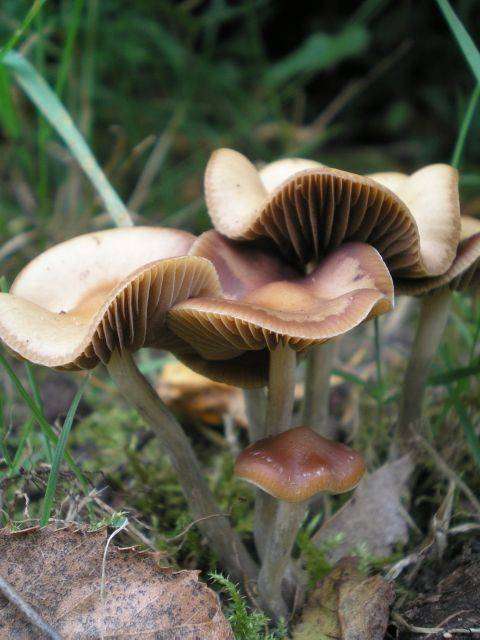

© Alan Rockefeller
1. Growing
Growing Procedure
In progress – Infos following soon
Growing Procedure
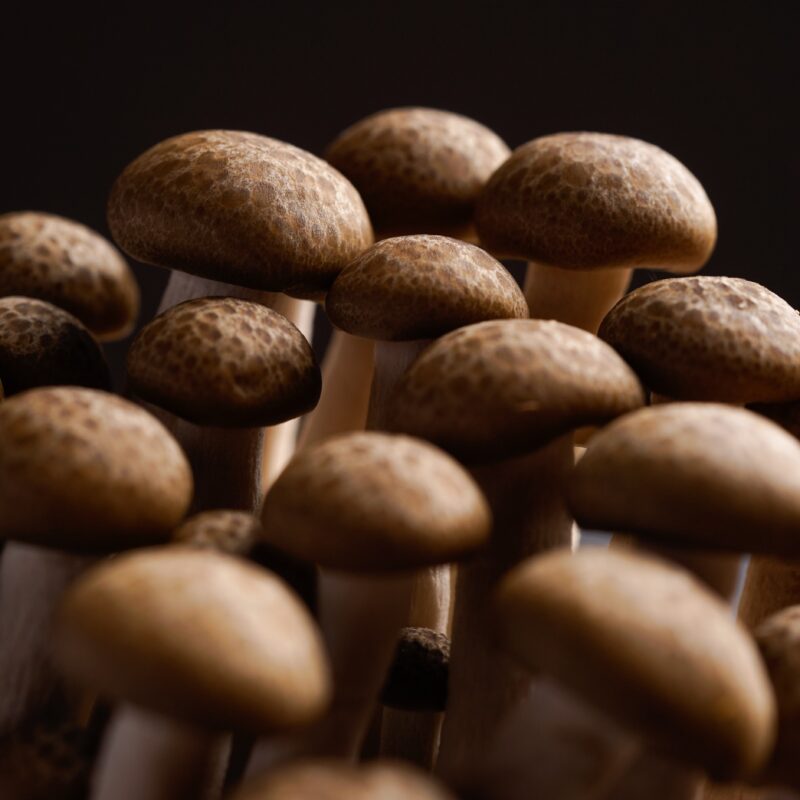
Psilocybe serbica, a little known mushroom native to Europe, can be cultivated using the following steps for indoor cultivation. For outdoor growing, follow our P. allenii guide with changed parameters.
Step 1: Preparing the Substrate
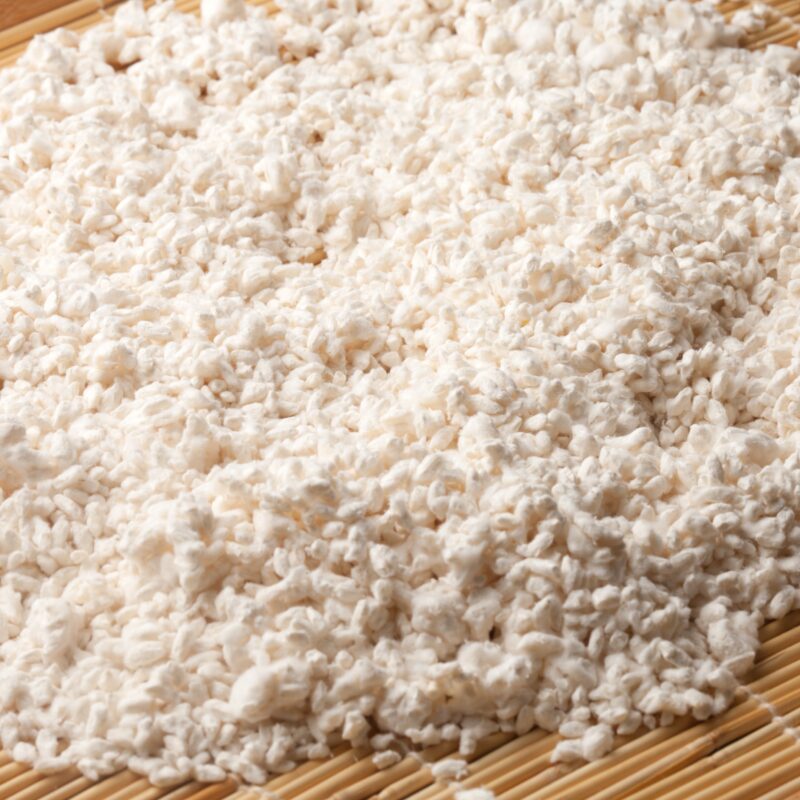
- Mix 2 parts vermiculite, 2 parts brown rice flour, and 1 part water in a large bowl.
- Fill wide-mouth glass jars with the substrate mixture, leaving about 3 cm (1 inch) of space at the top.
- Cover the jars with tin foil to prevent water from getting in.
- Sterilize the jars in a pressure cooker or Instant Pot for 30 minutes to kill any competing organisms.
- Allow the jars to cool down before proceeding to the next step.
Step 2: Inoculation
- Clean the area where you’ll be working with isopropyl alcohol to maintain sterility.
- Using a sterilized spore syringe, inject approximately 2 CCs of spore solution into each jar.
- Seal the jars and cover the top with tin foil.
- Repeat this process for each jar, ensuring cleanliness between each inoculation.
Step 3: Incubation
- Set up an incubator to create ideal conditions for the spawn run.
- Place the inoculated jars in the incubator, or if you have a suitable dark and warm spot in your house, use that instead.
- Check the jars every few days for signs of contamination and monitor the growth of white mycelium.
Step 4: Fruiting
- Once the jars are fully colonized with white mycelium, it’s time to initiate fruiting.
- Create a fruiting chamber by using a clear container that allows some airflow and maintains high humidity (>80%).
- Place the colonized jars inside the fruiting chamber and provide low levels of indirect light.
- Maintain fruiting parameter
- Spray the substrate with filtered or distilled water to keep it moist.
- Over time, mushrooms will start to grow from the colonized substrate.
- Harvest the mushrooms when they reach the desired size and maturity.
It’s important to prioritize safety and legality when engaging in any cultivation activities. Ensure you comply with local laws and regulations regarding the cultivation and use of psilocybin-containing mushrooms.
S
|
P
|
F
|
|
|---|---|---|---|
Temp |
18-24°C (64°-75°F) | 7-13°C (45-56°F) |
10-18°C (50-65°F) |
Relative Humidity % |
95-100 | 95-100 | 90-95 |
Duration d |
45-60 | 10-14 | 10-20 |
CO2 ppm |
>5000 | 1000-2000 | <1000 |
FAE per h |
0-1 | 4-6 | 4-8 |
Light lux |
– | 200-800 | 400-800 |
Growing
Agar Culture Media: MEA, MYPA, MYA, PDYA
Cropping Cycle: Two cops, 3-4 weeks apart
Containers for fruiting: Woodlogs, Treestemps
Biological efficiencies: medium
Substrates: wood, humus
Growing Characteristics
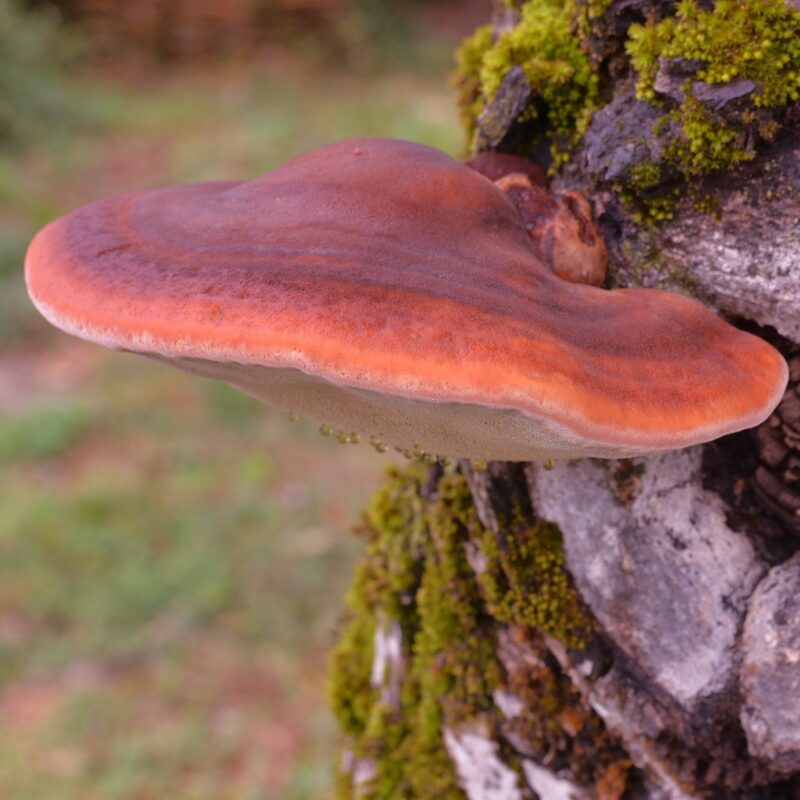
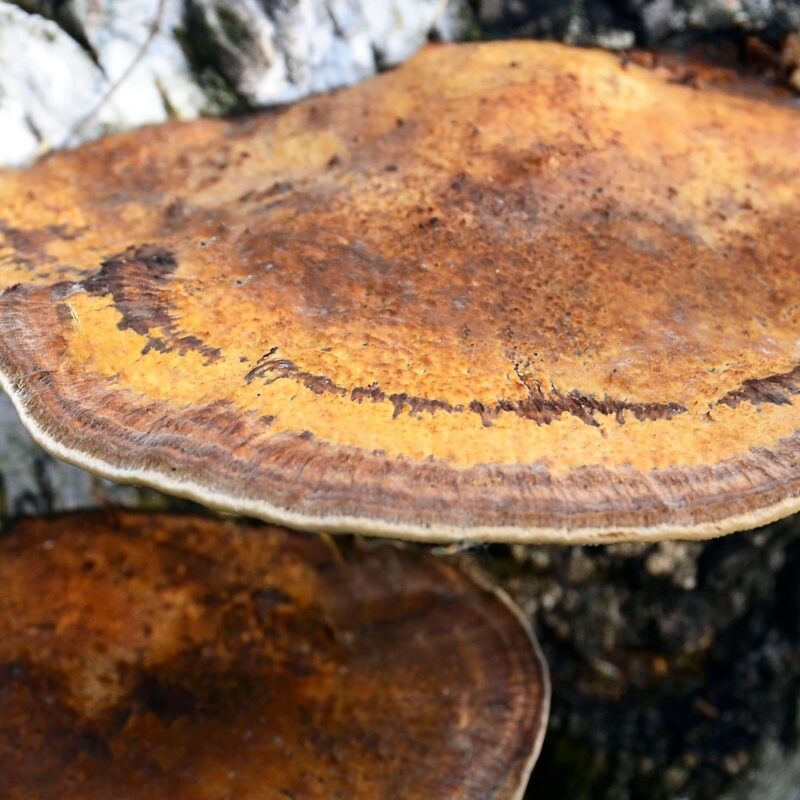
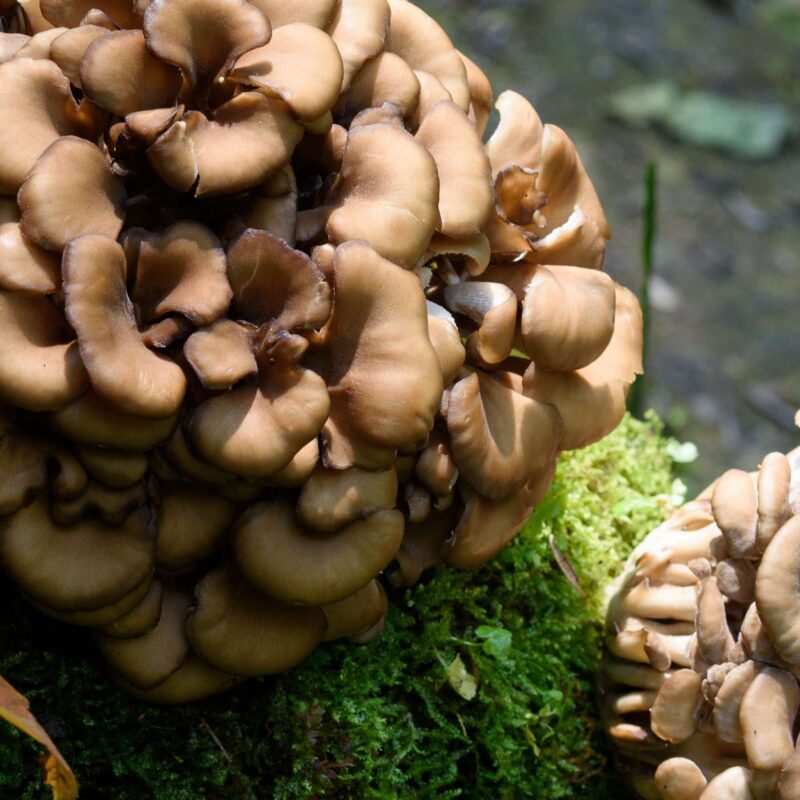
They all clearly visible brown and wavy. Also they grow grouped together.
Natural Habitat
Late summer to late fall
Deciduous forest, alluvial forest, calcareous soil, in moist forests or gardens, on dead wood, humus, later decomposers
Psilocybe cyanescens is found in North America, North Africa, and Europe. In Europe, finds have been reported in Sardinia, Serbia, Italy, France, the Netherlands, Great Britain, Switzerland, the Czech Republic, and Germany.
Psilocybe cyanescens thrives in warm areas of both hemispheres. Occurs singly to numerous in manure, well-fertilized soil, grassy areas, meadows, or pastures. It is actually a subtropical art that is also seen in southern Europe up to Hungary. There are reports of finds from Hawaii, Mexico, Java, Bali, and the south of France. Harvest time is from September to October.
Affiliate Partner
2. Identification
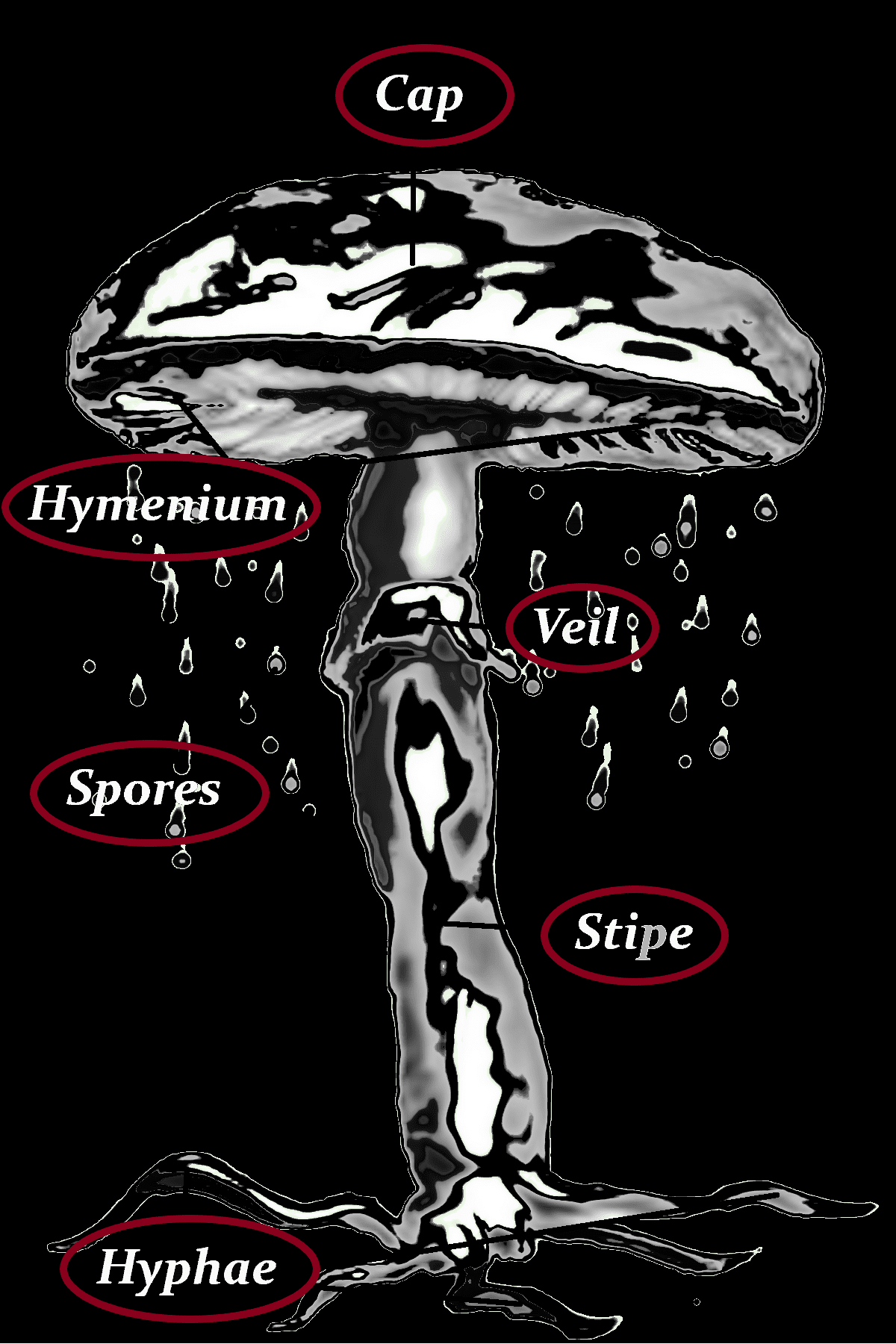
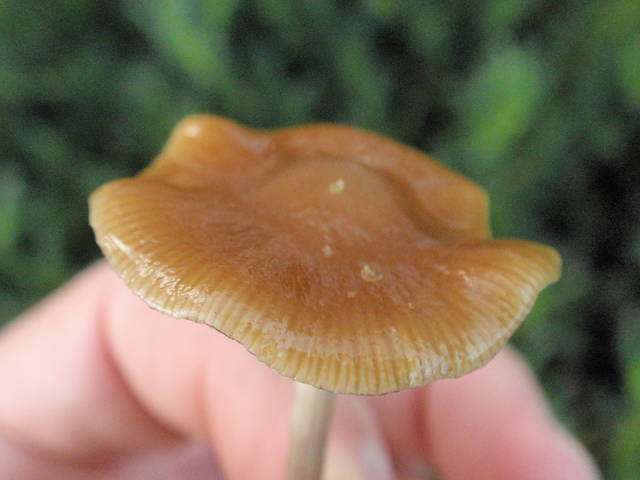
Cap
-2-4 (5) cm
-grayish brown, light brown, hazel
-pale ochre yellowish when dry
-hygrophanous
-greasy when wet
-hemispherical
-somewhat humped
-shallowly conical
-later shallowly convex
-greenish blue when injured
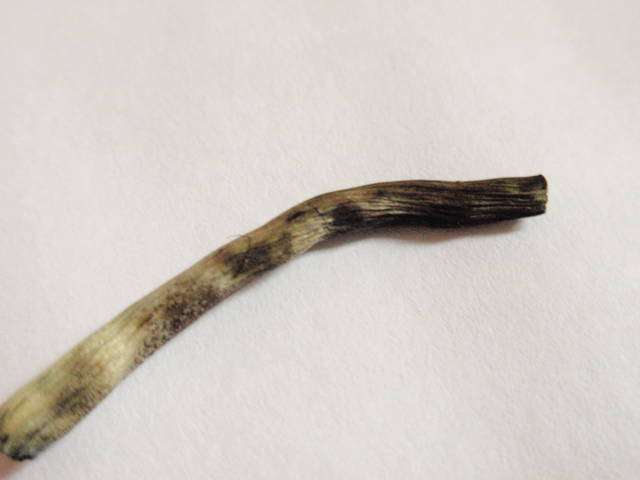
Stipe
-3-8 (11) cm high
-0.3-0.7 (1) cm thick
-light brownish, whitish
-white-fibrous-floccose
-usually darker brownish to base and strongly whitish overfibrous
-base with mycelium white-felted
-green-blue when pressed
Hyphae
Hymenium
-gray, gray-brown, cinnamon-brown, dark brown
-broadly adnate
-sometimes a little with tooth running down
-very distant standing
-spotted from the spores
-cutting lighter
-with intermediate lamellae
Spores
9-12 x 6-8 µm
-blackish brown, dark purplish to pinkish brown
Danger of confusion
PSILOCYBE SERBICA VAR. BOHEMICA, PANAEOLUS CYANESCENS, PSILOCYBE ALLENII, PSILOCYBE SEMILANCEATA, PROTOSTROPHARIA SEMIGLOBATA, PANAEOLUS PAPILIONACEUS, PANAEOLUS GUTTULATUS, PANAEOLUS FIMICOLA
Veil
-dark brown
-drooping
-grooved
3. Consuming
Dosis
There is an urgent warning against food experiments with Psilocybe cyanescens. Collecting, possessing and selling drug mushrooms is illegal in many countries around the world.
Depending on the particular strain, growth method, and age at harvest, psilocybe mushrooms can come in rather different potencies. It is recommended to weigh the actual mushrooms, better then counting them. 10% of the mushrooms mass is left, when dried. Take a look at Properties, to find out how potent they are.
Effect
The effect of Psilocybe cyanescens is said to be quite powerful. Everyone who has tried it raves about the extraordinarily plastic visions. Batik paintings by Javanese artists in the city of Yogyakarta give artistic expression to these colorful and heavily mythological visions.
Duration:
about 5-6 hours
Smell
-neutral to musty
Taste
-mild
Flesh
-brownish
-bluish when bruised
Composition
After the poisoning in Menton (France), the group around A. Hofmann detected 0.2% psilocybin in the Wavy Cap. However, due to the strong effect of the fungi, this concentration seems too low. Later, Sandoz Laboratories found 0.8% psilocybin and 1.2% psilocin in the mushroom species.
In Thailand by J.W. According to Stijve, all Psilocybe cyanescens collected contained 0.4-1.05% psilocin and only trace amounts of psilocybin; Serotonin was plentiful. A. Hofmann himself claims a content of 1.2% psilocin and 0.6% psilocybin, the highest content of these alkaloids ever found in a hallucinogenic mushroom.
4. Data
other names
cyans, Wave Cap, blue halos, blueing psilocybe, potent psilocybe, wavy-capped psilocybe, Blauender Kahlkopf, Blaugrünfleckender Kahlkopf, Blaufärbender Kahlkopf, blueleg brownie, Blauender Duengerling, Pan Cyan, Copelandia c. (Berkeley & Broome) Singer, Agaricus c. Berkeley & Broome, Faltenduengerling, Copelandia papilonacea (Bull.) Bres., Campanularius anomalus Murrill, P. anomalus (Murrill) Sacc. & Trott., Campanularius westii Murrill, P. westii (Murrill), Copelandia westii (Murrill) Sing., Copelandia c. (Berkeley & Broome) Boedijn, Jambur
| Kingdom | Fungi |
|---|
| Division | Basidiomycota |
| Class | Agaricomycetes |
| Order | Agaricales |
| Family | Hymenogastraceae |
| Genus | Psilocybe |
| Species | P. cyanescens |
| Ecology | saprotrophic |